Industrial Engineering
Editor's pick
Research Article
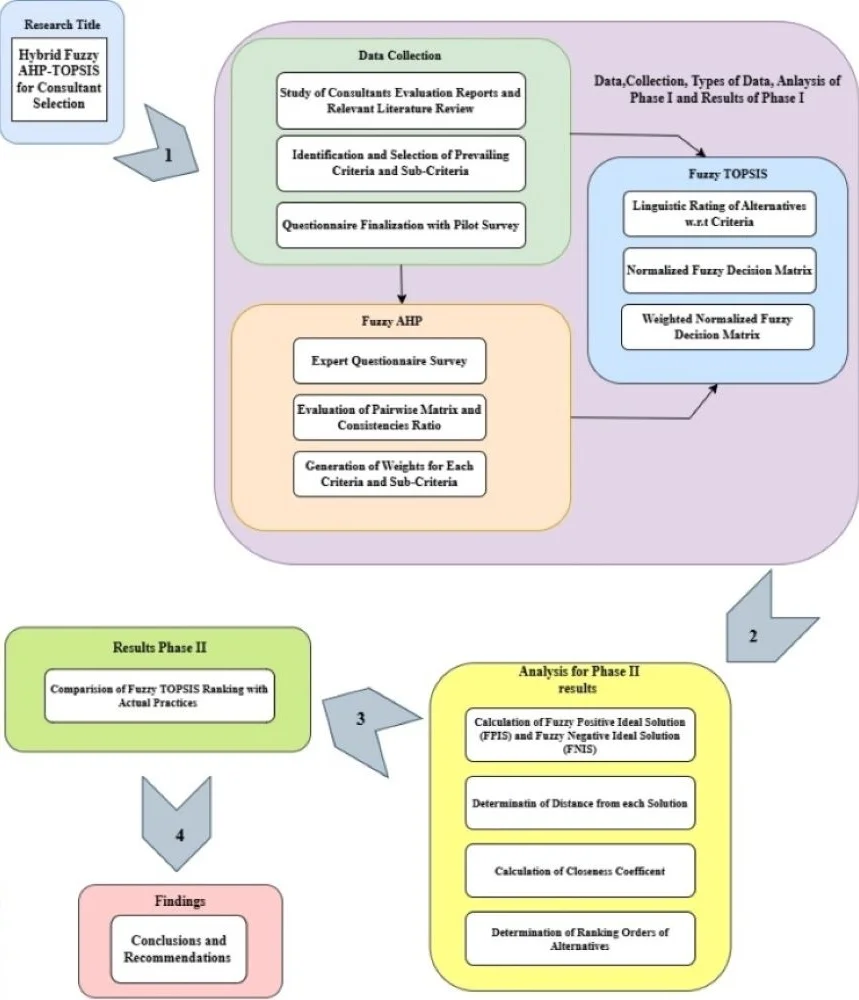
Enhancing technical proposal evaluation in consultant selection in Department of Water Resources and Irrigation, Nepal: a fuzzy analytic hierarchy process and fuzzy TOPSIS
By Nischal Silwal, Subash Kumar Bhattarai, Dinesh Sukamani
In today's dynamic construction landscape, where challenges like complexity, costs, and uncertainties loom large, the selection of consultants emerges as a pivotal factor for project triumph. Among the array of methods available, Quality and Cost Based Selection (QCBS) stands out for its holistic approach, considering both technical prowess and financial considerations. Yet, amidst its structured framework, the evaluation of technical proposals within QCBS often grapples with subjectivity, despite the presence of well-defined criteria. This study boldly tackles this challenge head-on by delineating common criteria and sub-criteria for consultant selection within the esteemed Department of Water Resources and Irrigation (DWRI). Leveraging the innovative Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP), our endeavor is to ascertain the relative significance of these criteria and sub-criteria. Through the fusion of Fuzzy AHP and Fuzzy Techniques for Order Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution (TOPSIS), our study aspires to revolutionize consultant ranking methodologies. The ingenious application of Fuzzy AHP empowers us to derive independent weights for criteria and sub-criteria, thereby embracing the inherent ambiguity and nuances of qualitative factors. Subsequently, employing Fuzzy TOPSIS, we aim to systematically rank consultant alternatives based on their Closeness Coefficients, heralding a paradigm shift in evaluation paradigms. Through this groundbreaking hybrid approach, our study endeavors to elevate the consultant selection process, ensuring an impeccable alignment of chosen consultants with project requisites and benchmarks. By dispelling the shadows of subjective decision-making uncertainties, our research holds the promise of ushering in a new era of excellence in the realm of construction projects under the aegis of the Department of Water Resources and Irrigation.
December 30, 2024
Applied Physics
Most cited
Research Article
A conversion guide: solar irradiance and lux illuminance
By Peter R. Michael, Danvers E. Johnston, Wilfrido Moreno
December 4, 2020
Applied Physics
Most cited
Research Article
Fault diagnosis and health management of bearings in rotating equipment based on vibration analysis – a review
By Adnan Althubaiti, Faris Elasha, Joao Amaral Teixeira
November 26, 2021
Applied Mathematics
Most cited
Research Article
A convolutional neural network method based on Adam optimizer with power-exponential learning rate for bearing fault diagnosis
By Youming Wang, Zhao Xiao, Gongqing Cao
June 30, 2022
Applied Mathematics
Most cited
Research Article
A review on wind turbines gearbox fault diagnosis methods
By H. Gu, W. Y. Liu, Q. W. Gao, Y. Zhang
January 27, 2021
Applied Mathematics
Maintenance, Reliability and Condition Monitoring
Research Article
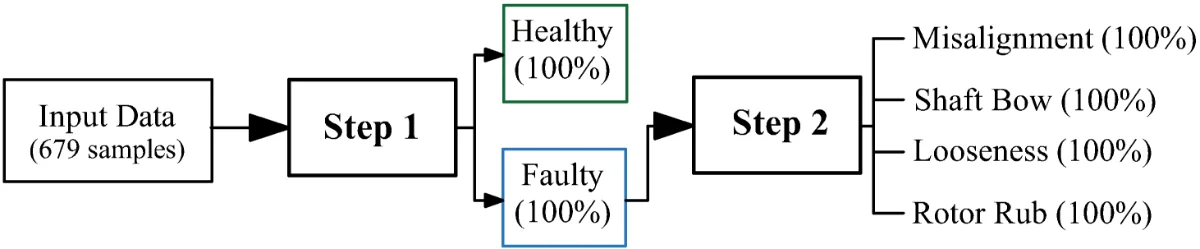
Robust vibration-based faults diagnosis machine learning model for rotating machines to enhance plant reliability
Plant availability and reliability can be improved through a robust condition monitoring and fault diagnosis model to predict the current status (healthy or faulty) of any machines and critical assets. The model can then predict the exact fault for the faulty asset so that remedial maintenance can be carried out in a planned plant outage. Nowadays, the artificial intelligence (AI)-based machine learning (ML) model seems to be current trend to meet these requirements. Hence, the paper is also proposing such vibration-based faults diagnosis ML model through an experimental rotating rig. Here, the 2-Steps approach is used with the ML model to easy the industrial operation and maintenance process. The Step-1 provides the information about the asset health status such as healthy or faulty. The Step-2 then identifies the exact nature of fault to aid the decision making for the fault rectification and maintenance activities to avoid the risk of failure and enhance the reliability.
June 30, 2021
Applied Mathematics
Research Article
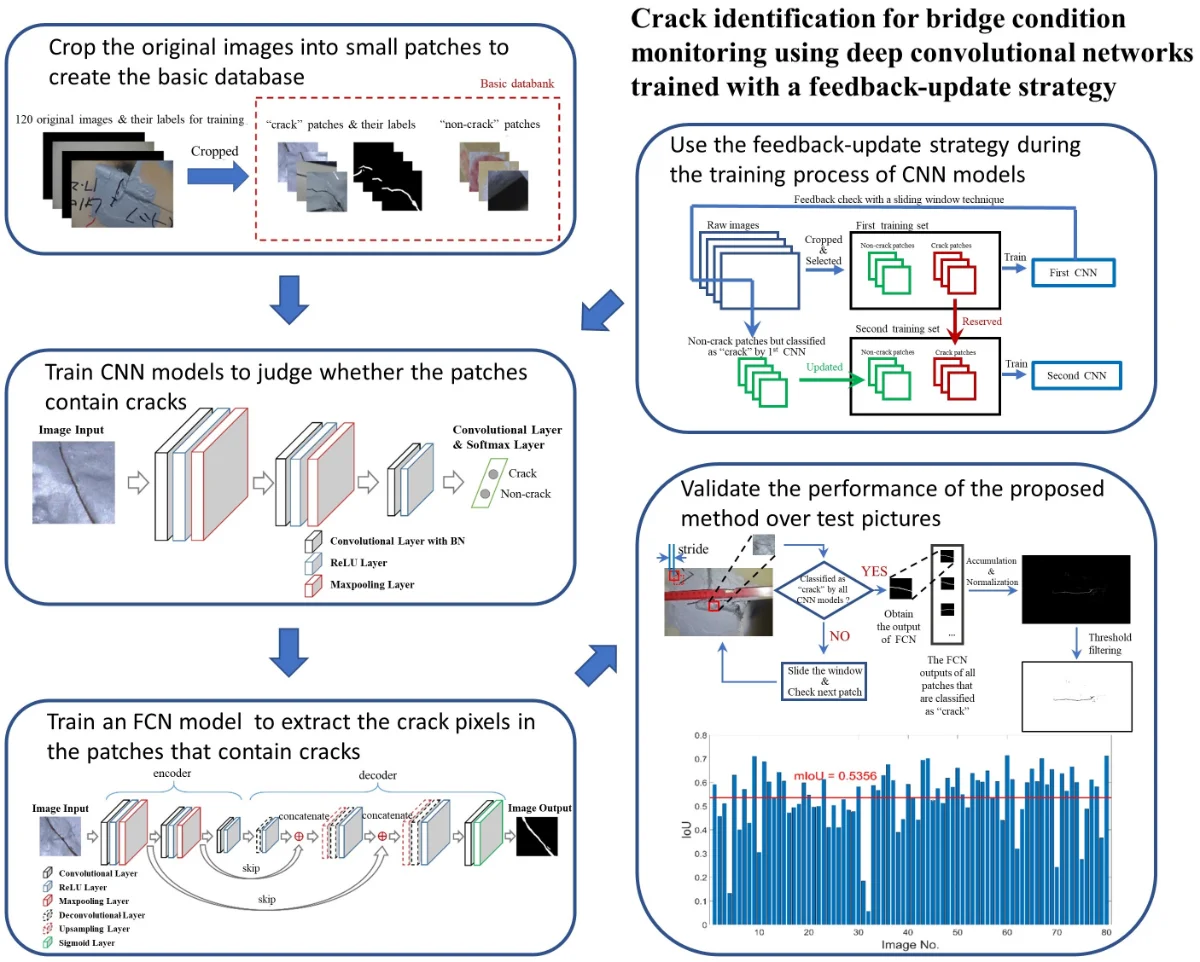
Crack identification for bridge condition monitoring using deep convolutional networks trained with a feedback-update strategy
Orthotropic steel bridge decks and steel box girders are key structures of long-span bridges. Fatigue cracks often occur in these structures due to coupled factors of initial material flaws and dynamic vehicle loads, which drives the need for automating crack identification for bridge condition monitoring. With the use of unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), the acquirement of bridge surface pictures is convenient, which facilitates the development of vision-based bridge condition monitoring. In this study, a combination of convolutional neural network (CNN) with fully convolutional network (FCN) is designed for crack identification and bridge condition monitoring. Firstly, 120 images are cropped into small patches to create a basic dataset. Subsequently, CNN and FCN models are trained for patch classification and pixel-level crack segmentation, respectively. In patch classification, some non-crack patches that contain complicated disturbance information, such as handwriting and shadow, are often mistakenly identified as cracks by directly using the CNN model. To address this problem, we propose a feedback-update strategy for CNN training, in which mistaken classification results of non-crack data are selected to update the training set to generate a new CNN model. By that analogy, several different CNN models are obtained and the accuracy of patch classification could be improved by using all models together. Finally, 80 test images are processed by the feedback-update CNN models and FCN model with a sliding window technique to generate crack identification results. Intersection over union (IoU) is calculated as an index to quantificationally evaluate the accuracy of the proposed method.
August 6, 2021
Applied Mathematics
Research Article
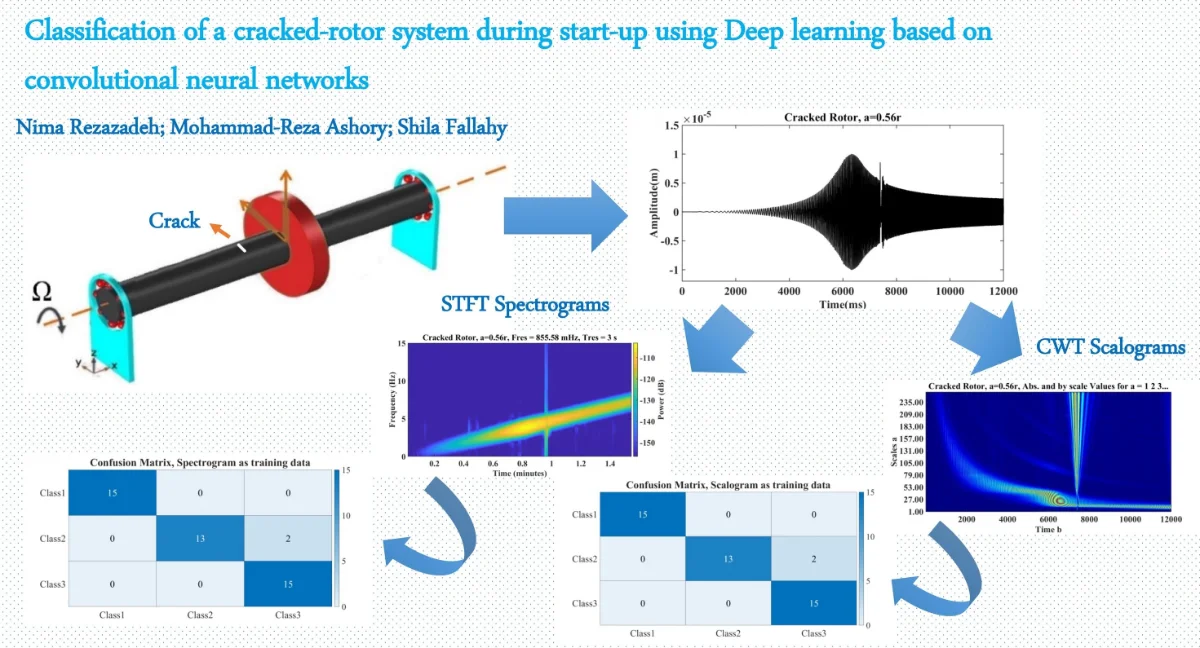
Classification of a cracked-rotor system during start-up using Deep learning based on convolutional neural networks
This article addresses an improvement of a classification procedure on cracked rotors through Deep learning based on convolutional neural networks (CNNs). At first, a cracked rotor-bearing system is modeled by the finite element method (FEM), then throughout its start-up, the related time-domain responses are calculated numerically. In the following, as a pre-processing stage, continuous wavelet transform (CWT) and Short-time Fourier transform (STFT) are applied on the three various health conditions, i.e. without crack, shallow-cracked, and relatively deep-cracked shafts. The plots of CWT’s coefficients and STFT’s in these various classes are used as the input dataset in Deep learning based on CNNs and the three classes are introduced as the output. AlexNet with 25 layers is employed as the network. The results of the testing phase demonstrated that not only this expanded method has a reasonable capacity in the classification of cracked and healthy rotors, but it also can classify cracked rotors with different crack depths with a negligible error.
December 15, 2021
Applied Mathematics
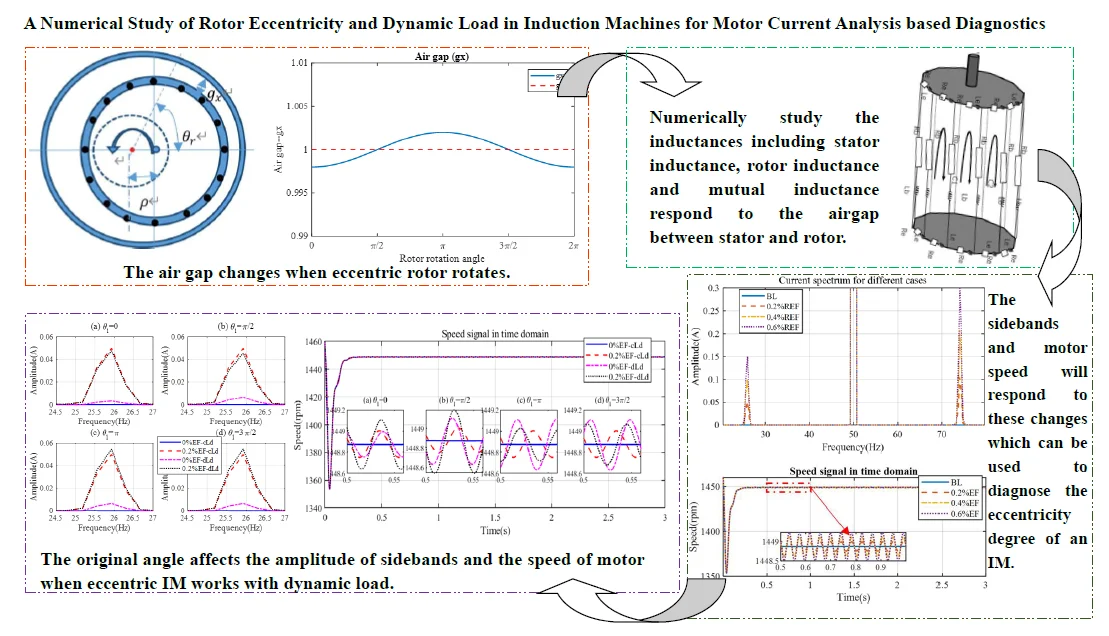
Research Article
A numerical study of rotor eccentricity and dynamic load in induction machines for motor current analysis based diagnostics
The asymmetry in the manufacturing and assembling is the common issue of rotor systems. Different degrees of errors are inevitable in alternating current (AC) motors, which causes degraded performances. Furthermore, around 80 % of mechanical faults link to rotor eccentricity. The eccentricity faults (EFs) generate excessive mechanical stress and then lead to fatigue in the other parts of the motor. Motor current signal analysis (MCSA) can be used to diagnose induction machine (IM) faults. As the EF leads to an unequal air gap when the rotor rotates, the inductance of IM also responds to the EF. Moreover, the dynamic load is a typical situation due to residual dynamic unbalance and misalignment. To study how EFs and dynamic load affect the stator current. The current model of symmetrical motor, asymmetrical motors with three-level EFs and with dynamic load are investigated numerically. The correctness of models is verified through experimental study. The results show the level of EF affects the sideband peak values significantly in the stator current spectrum. These findings will provide a foundation for the accurate diagnosis of motor health conditions.
August 6, 2021
Applied Mathematics
Maintenance, Reliability and Condition Monitoring
Devoted to the fields of plant maintenance, asset management, reliability, condition monitoring and related areas
APC
Free of charge
Best of Theme
Most cited
Research article
August 15, 2020
Bearing fault diagnosis based on improved VMD and DCNN
By Ran Wang, Lei Xu, Fengkai Liu
Most cited
Research article
September 30, 2019
Fault diagnosis method for energy storage mechanism of high voltage circuit breaker based on CNN characteristic matrix constructed by sound-vibration signal
By Shutao Zhao, Erxu Wang, Jiawei Hao
Most cited
Research article
June 26, 2022
Recent advancements of signal processing and artificial intelligence in the fault detection of rolling element bearings: a review
By A. Anwarsha, T. Narendiranath Babu
Most cited
Research article
December 31, 2019
Damage identification of bridge structure based on frequency domain decomposition and strain mode
By Jiaquan Wu, Hongyan Li, Fei Ye, Kun Ma
You might also like
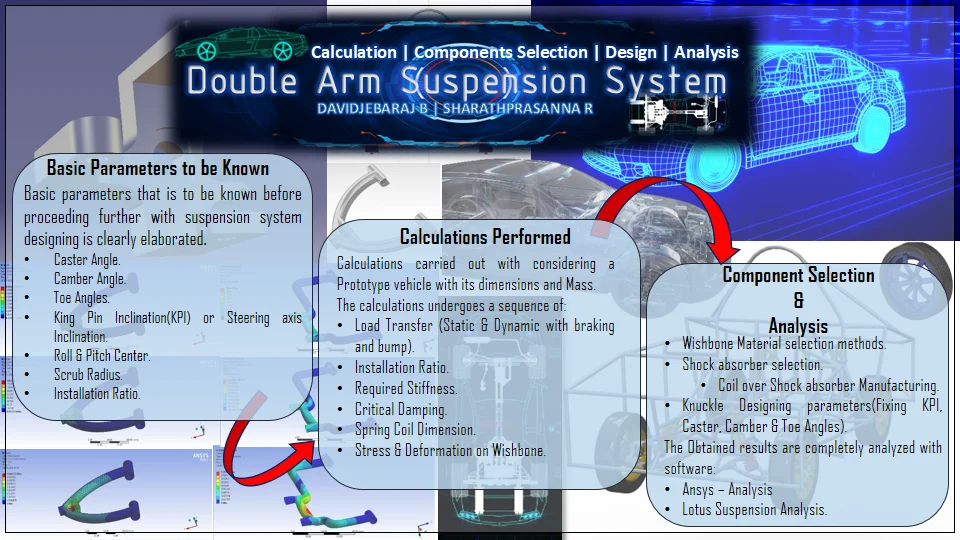
Most downloaded
Research Article
Design and calculation of double arm suspension of a car
By David Jebaraj B, Sharath Prasanna R
Suspension system is one of the challenging portions in designing a vehicle. The complete stability of the vehicle under dynamic conditions depends on the suspension system of the vehicle. Suspension system of a vehicle is interlinked with other systems such as steering, Wheels and Brakes. The main objective of this document is to provide complete guidance in designing and calculation of an independent suspension system with double control arms. The required parameters are calculated on considering a prototype vehicle with gross weight of 350 kg such as required stiffness of shock absorbers, Ride frequency, Motion ratio, Coefficient of damping etc. A CADD model was made with CATIA v5 r20 and SOLIDWORKS on the basis of calculations obtained and stress analysis was carried out for this model in various software such as Ansys. The complete assembled model was tested in LOTUS Shark and the result was obtained.
June 30, 2020
Industrial Engineering
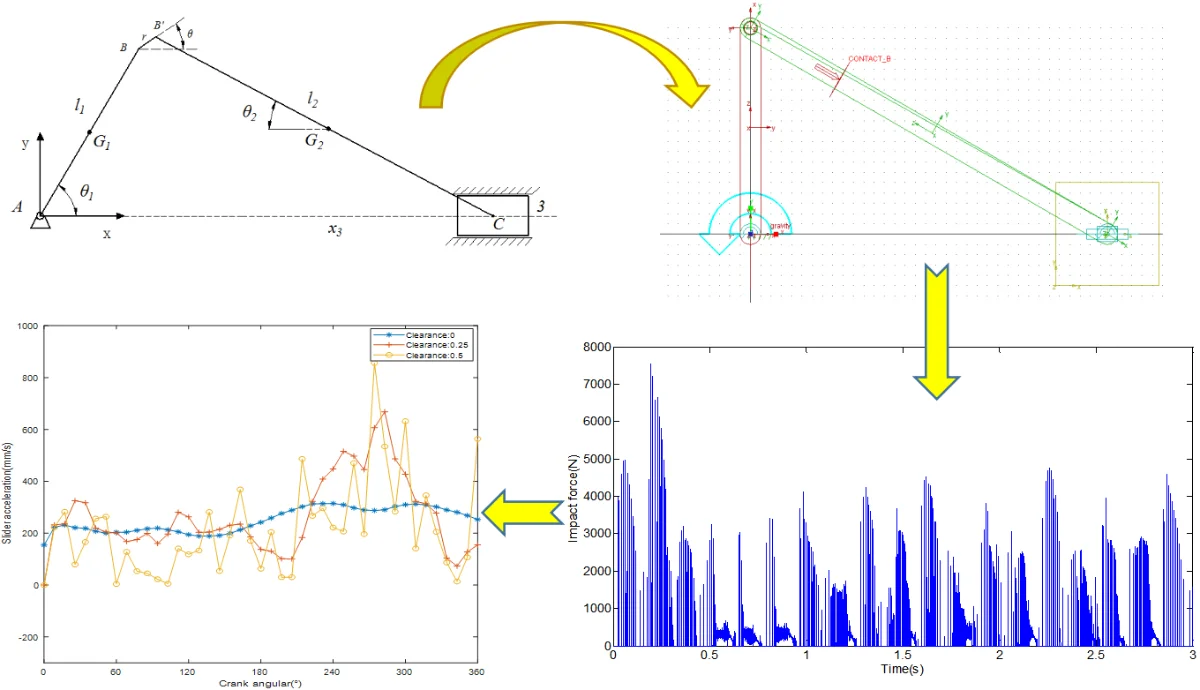
Most downloaded
Research Article
Dynamic analysis of slider-crank mechanism with clearance fault
By Shungen Xiao, Mengmeng Song, Zexiong Zhang
In this paper, the dynamic behavior of the slider-crank mechanism with clearance fault is investigated. The revolute joint with clearance is equivalent to a virtual massless rod, and then the dynamic equation of the crank slider mechanism with clearance is established by the Lagrangian method. In addition, a three-dimensional dynamic model of the crank slider mechanism with clearance is also established by ADAMS. The numerical results show that the clearance affects the displacement and velocity response of the crank-slider mechanism in a weak way, but influences the acceleration response of the mechanism in a significant manner. Due to the existence of the clearance, the revolute joint of the mechanism produces a rub-impact phenomenon, and the larger the clearance, the greater the impact strength. During the rub-impact process, there are three kinds of motion states of separation, collision and contact occur.
November 28, 2019
Applied Mathematics
Design, analysis and fabrication of a fully articulated helicopter main rotor system
This study describes an integrated framework in which the basic elements of Aerospace Engineering (performance, aerodynamics and structure) and functional elements (suspension, visibility and production) are integrated and considered. In this study, a fully functional rotor system has been fabricated that can be used as one of the training resources for Aeronautical students. For making the rotor system, various parts of the system have been designed on Solidworks and complete mechanism has been simulated with ANSYS. System analysis has been done at various RPM's and Angles of Attack (AOA). In terms of merit the right items have been selected and processed to provide them with the right shape. In terms of the design and implementation, various machines such as gas welding, arc welding, CNC milling and radial machinery have been used. Certain parts such as electric motors, linear actuators and loading cells have been used. All the fabricated components and electric motor, actuator, load cells are then assembled. This rotor system can produce less lift due to high dead weight and low power motor and having some safety issues.
FE analysis and experimental determination of a shaft deflection under three-point loading
Increasing industrial demand for new products including advanced production technology leads to substantial natural resources consumption. Furthermore, huge environmental pollution and emerging environmental legislation motivate the machine tools industry as one of the major resource consumers on a global scale to develop methods for more sustainable use of the Earth's resources. Machine tools re-engineering concerning design and failure analysis is an approach by which outdated machines are upgraded and restored to like-new machines. To evaluate the mechanical failure of the used machine components and to ensure their reliable future performance, it is essential to make material, design, and surface investigations. In this paper, an experimental approach based on the principle of a three-point bending test is presented to evaluate the shaft elastic behavior under loading. Moreover, finite element analysis and numerical integration method are used to determine the maximum linear deflection and bending stress of the shaft. Subsequently, a comparison between the results is made. In conclusion, it was found that the measured bending deflection and stress were well close to the admissible design values. Therefore, the shaft can be used again in the second life cycle. However, based on previous surface tests conducted, the shaft surface needs re-carburizing and refining treatments to ensure the reliable performance of the surface.