What's new
Editor's pick
Research Article
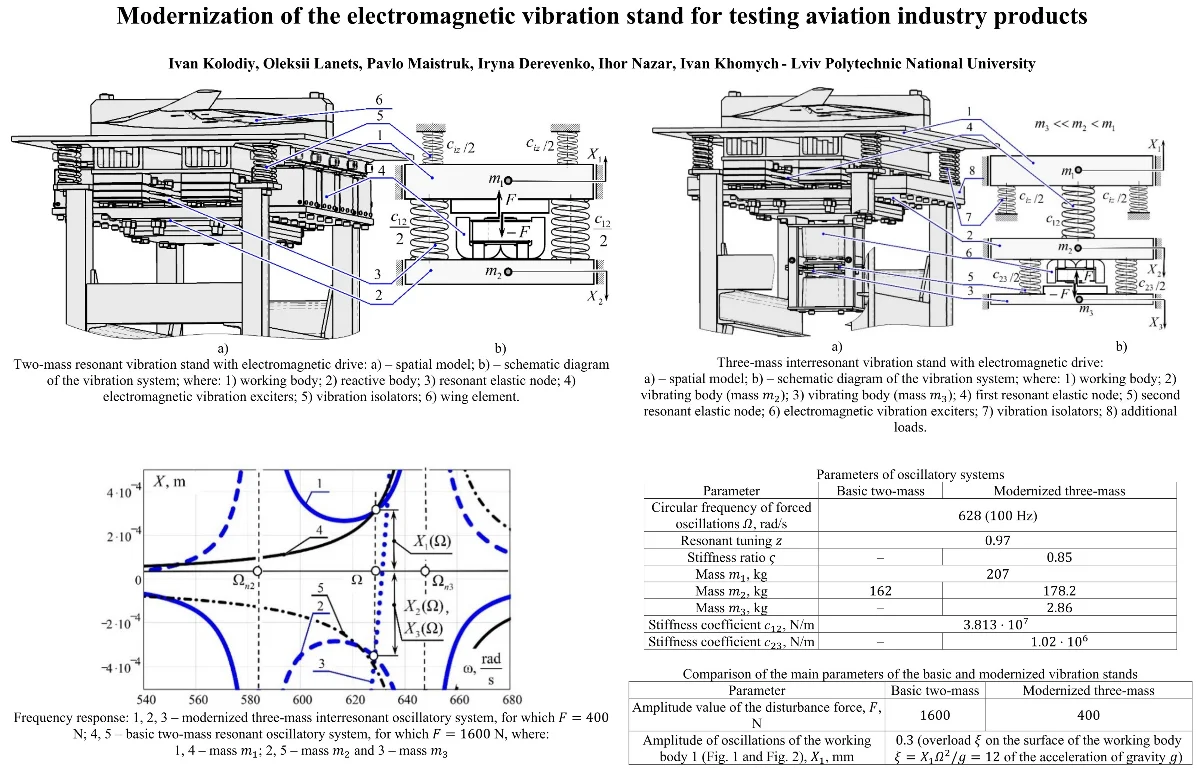
Modernization of the electromagnetic vibration stand for testing aviation industry products
By Ivan Kolodiy, Oleksii Lanets, Pavlo Maistruk, Iryna Derevenko, Ihor Nazar, Ivan Khomych
The article presents a methodology for modernizing a two-mass resonant electromagnetic vibration stand for testing parts of the aviation industry for vibration resistance. The main goal of the modernization is to provide a significantly lower disturbance force from electromagnetic vibration exciters to set the working body in motion. For this purpose, by introducing a third oscillating mass into the two-mass mechanical system, the interresonant mode of operation of the vibration stand is ensured. Analytical dependencies are presented that reveal the methodology for calculating inertial and stiffness parameters that ensure the transformation of a two-mass resonant vibration system into a three-mass interresonant vibration system. A specific example demonstrates the implementation of the proposed approach in the modernization of the design. The amplitude-frequency characteristics of the basic two-mass resonant and modernized three-mass interresonant vibration systems are constructed. It has been confirmed that to ensure the specified amplitude of oscillations of the working body in the modernized design, 4 times less disturbing force from electromagnetic vibration exciters (400 N) is required.
September 30, 2025
Vibration Engineering
Research Article
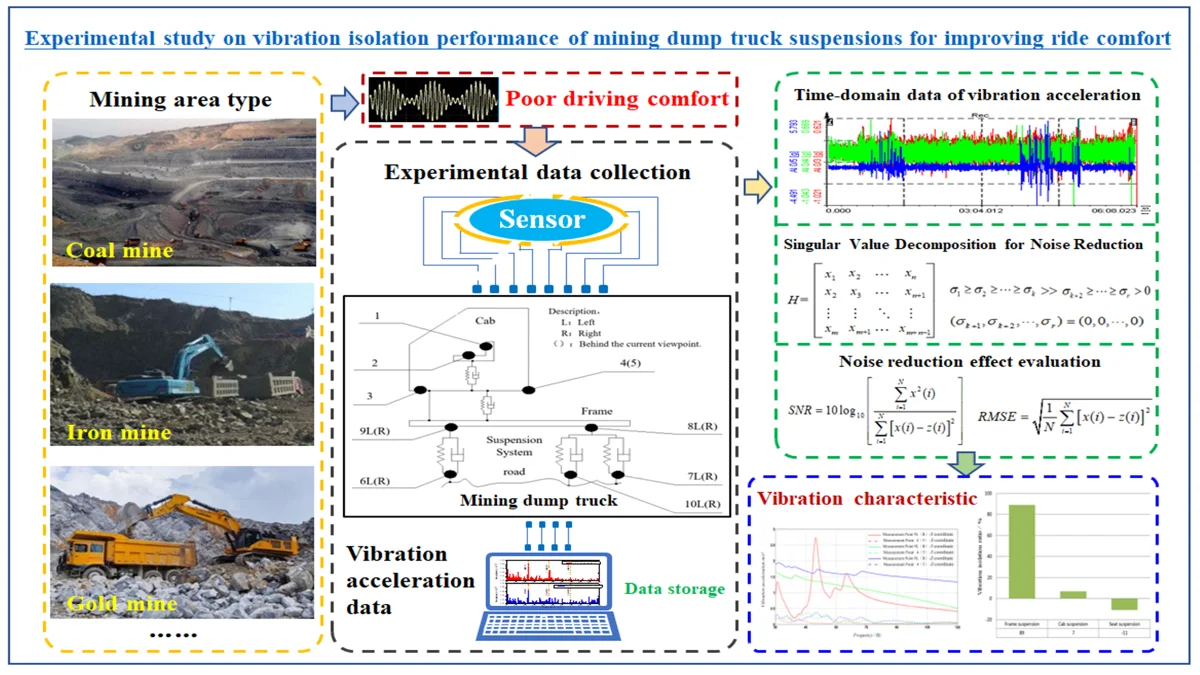
Experimental study on vibration isolation performance of mining dump truck suspensions for improving ride comfort
This study addresses the challenge of reducing the transmission of low-frequency road excitation vibrations to the cab of mining dump trucks to enhance ride comfort. Given the harsh working conditions of these vehicles, a novel methodology combining experimental data collection and advanced signal processing techniques was developed. The research established a comprehensive vibration testing program aligned with earth-moving machinery standards, collecting vibration acceleration data under both idling and full-load operation at 35 km/h. To improve data accuracy, Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) was employed to denoise the experimental vibration data, effectively mitigating environmental interference. Subsequent Fourier transform analysis revealed the vibration energy transfer patterns of the vehicle suspension system in the frequency domain. The results indicated a significant vibration isolation rate of 89 % for the frame suspension system, contrasting with only 7 % for the cab suspension system. Notably, the cab seat suspension system was found to amplify low-frequency road excitations. Compared to previous methods, this study innovatively integrates SVD and Fourier transform techniques to provide a more accurate and detailed understanding of vibration transmission. The key result of achieving an 89 % vibration isolation rate for the frame suspension system demonstrates the effectiveness of the proposed methodology. This study offers practical optimization directions for improving suspension system performance and ride comfort in mining dump trucks, outperforming traditional approaches by providing a more comprehensive analysis and actionable insights for vibration isolation. The findings also serve as valuable references for addressing similar engineering challenges in heavy machinery.
November 24, 2025
Vibration Engineering
Research Article
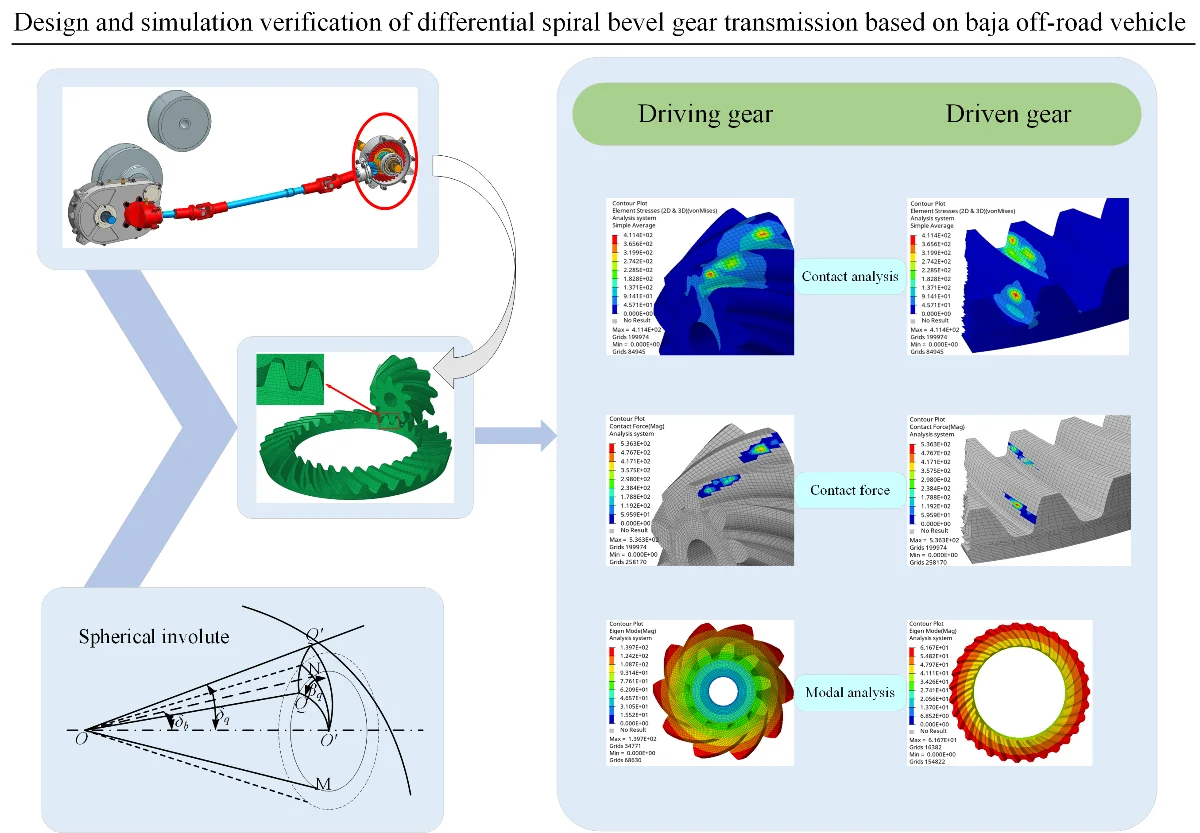
Design and simulation verification of differential spiral bevel gear transmission based on baja off-road vehicle
The differential spiral bevel gear of Baja off-road vehicle is designed and verified. Based on the competition rules and vehicle transmission parameters, the key geometric parameters of the gear pair are determined, and the three-dimensional model and finite element analysis software are established by UG for static contact analysis and modal analysis. The results show that the maximum contact stress of the tooth surface is 411.4 MPa, and the natural frequency of the gear pair is much higher than the excitation frequency of the system, which can effectively avoid the resonance risk. Through analysis and verification, it meets its application conditions.
November 24, 2025
Informatics
Research Article
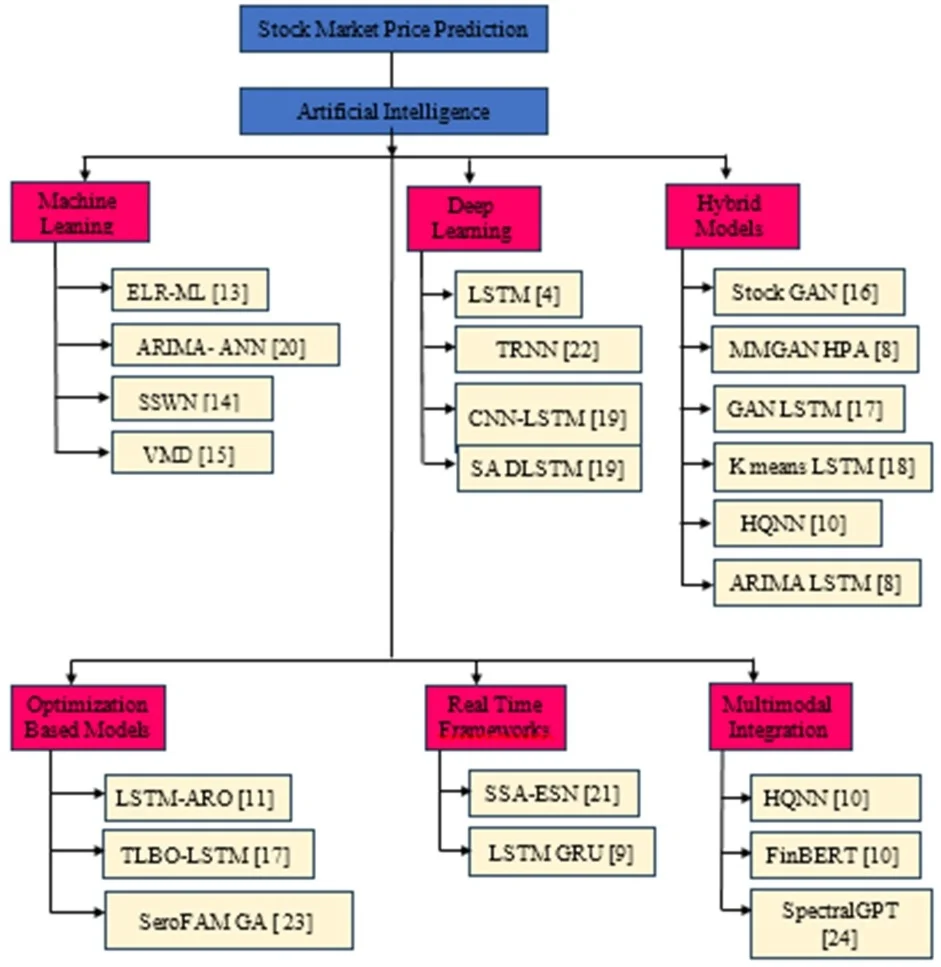
Artificial intelligence-based stock market price prediction, a review
The stock market, a cornerstone of the global financial system, is characterized by its dynamic and volatile nature, which makes accurate price-trend prediction challenging. However, traditional statistical models often fail to capture this complexity. Recent advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI), particularly Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL), have transformed stock market forecasting by using diverse datasets and algorithms. This review examines recent studies on AI methodologies for stock market price trend prediction models by analyzing architectures, datasets, performance metrics, and limitations, with a focus on hybrid models, sentiment analysis, and dataset diversity. Hybrid approaches, including the Multi-Model Generative Adversarial Network Hybrid Prediction Algorithm (MMGAN-HPA), K-means long short-term memory (LSTM), and LSTM autoregressive output (LSTM-ARO), improve predictive accuracy by combining statistical methods with deep learning. Sentiment analysis models such as Stock Senti WordNet (SSWN) and Hybrid Quantum Neural Network (HQNN) integrate social media sentiment to capture market dynamics. Real-time frameworks that use stream processing show promise for high-frequency trading applications. This review addresses key challenges including data noise, nonstationarity, overfitting risks, and black-box model interpretability. Solutions include GAN-based synthetic data generation, transformer-based architectures such as SpectralGPT, and optimization techniques for computational efficiency. This review provides a taxonomy of AI-based approaches, while identifying gaps for future research. These findings highlight the potential of AI in financial forecasting while emphasizing the need for interdisciplinary collaboration to address its limitations in data quality, methodology, interpretability, and ethics.
November 12, 2025
Informatics
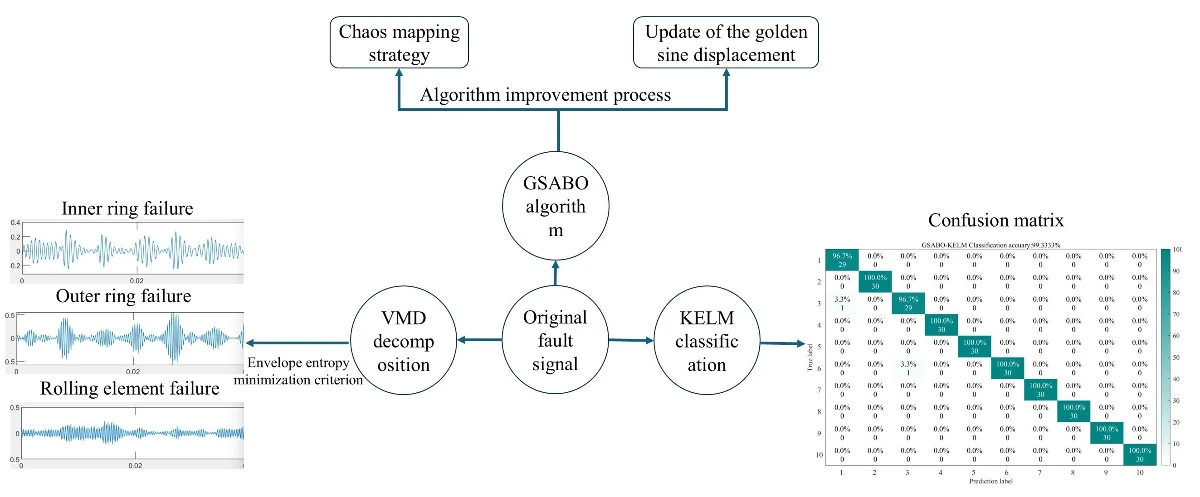
Research Article
Application of GSABO-VMD-KELM in rolling bearing fault diagnosis
To address the difficulties in extracting fault features of rolling bearings and the low diagnostic accuracy, a fault diagnosis method for rolling bearings is proposed. This method integrates the Golden Sine Algorithm (GSA) with the Subtraction-Average-Based Optimizer (SABO) to form a Golden Sine Improved SABO Optimization Algorithm (GSABO). The GSABO algorithm is used for parameter optimization of Variational Mode Decomposition (VMD) and Kernel Extreme Learning Machine (KELM) in the fault diagnosis process. Firstly, the chaotic mapping strategy is used to optimize the population initialization of the Subtractive Clustering-Based Adaptive Optimization (SCAO) algorithm, enhancing population diversity. Secondly, the Golden Sine Algorithm (GSA) is integrated to improve the displacement algorithm, enhancing global search capability and effectively avoiding getting trapped in local optima. Then, the GSABO-VMD (Golden Sine Algorithm-Based Optimized Variational Mode Decomposition) is employed to decompose the rolling bearing fault signals, and the envelope entropy minimum criterion is used to select the effective modal components. Finally, time-frequency domain indicators of the selected modal components are computed to form a feature matrix, which is then input into GSABO-KELM (Golden Sine Algorithm-Based Optimized Kernel Extreme Learning Machine) for fault classification and recognition. Experimental analysis shows that compared to the unmodified SABO algorithm, GSABO has significant advantages in terms of escaping local optima, convergence speed, and accuracy. When compared with other traditional algorithms, GSABO-VMD-KELM achieves recognition accuracies of 99.3333 % and 99.0476 % on bearing data from Case Western Reserve University (CWRU) and Xi'an Jiao tong University (XJTU), respectively. This demonstrates the accuracy and superiority of the algorithm and provides valuable insights for engineering applications in rolling bearing fault diagnosis.
October 31, 2025
Applied Mathematics
Latest from engineering
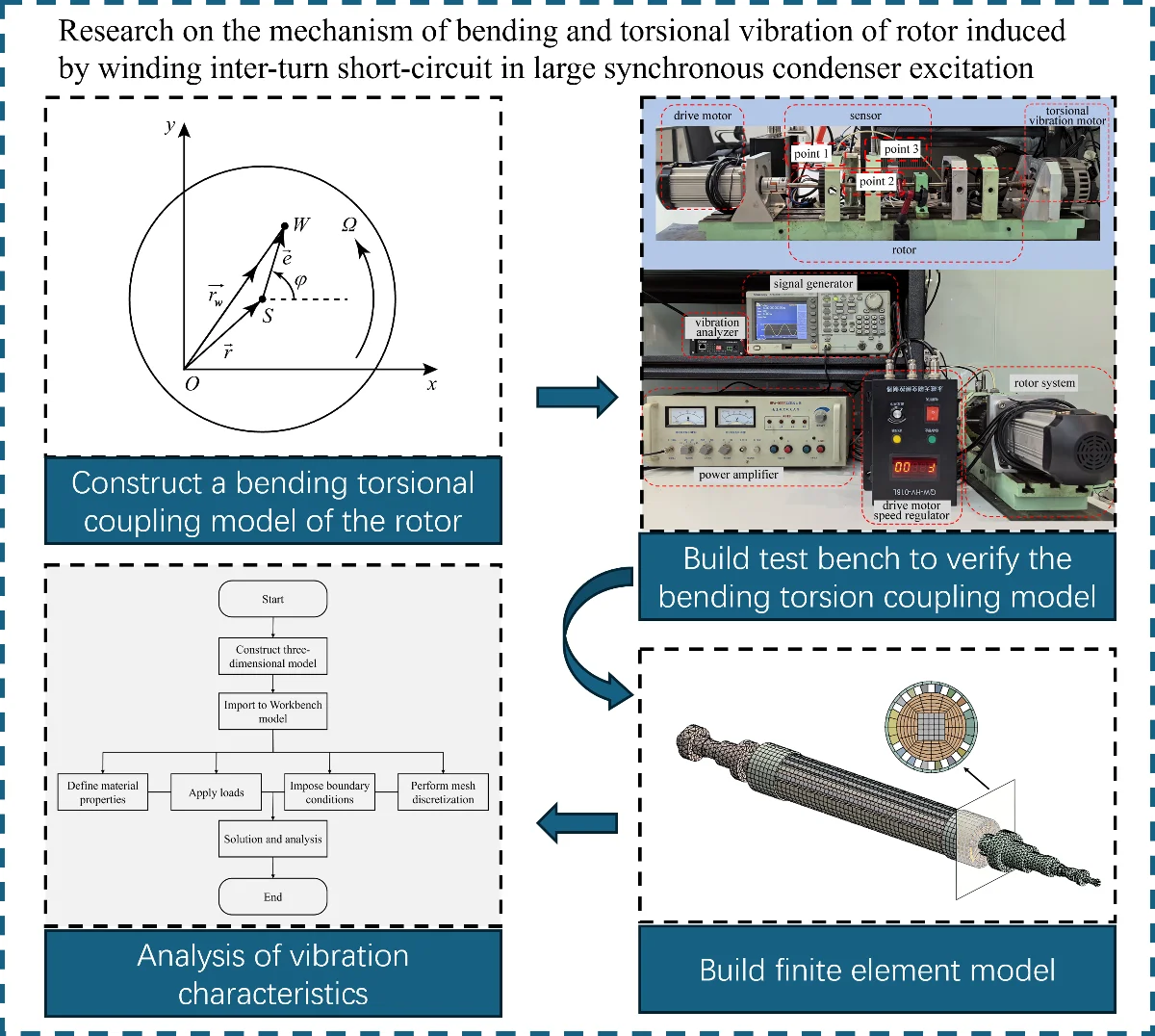
Research Article
Research on the mechanism of bending and torsional vibration of rotor induced by winding inter-turn short-circuit in large synchronous condenser excitation
The synchronous condenser plays a crucial role in reactive power compensation and voltage support in ultra-high voltage direct current power grids. Vibration is a key bottleneck for the safe and stable operation of the synchronous condenser, especially rotor vibration resulting from electromagnetic torque caused by inter-turn short-circuit. This article takes a 300 MV large synchronous condenser as the research object, and studies the influence of electromagnetic torque caused by inter-turn short-circuit on the vibration of the rotor. Through theoretical analysis and finite element simulation, a theoretical model and a finite element model of rotor bending-torsional coupled vibration were established, and the accuracy of the theoretical model was validated experimentally. The results show that: The first three bending frequencies are 11.93 Hz, 31.27 Hz, and 89.46 Hz; Under both static and dynamic imbalance conditions, the vibration amplitude of the rotor increases with the increase of the shorted turn ratio; The vibration amplitude before and after being stimulated under dynamic unbalance is larger than that under static imbalance. The research results can provide a theoretical basis for the design and safe operation and maintenance of the synchronous condenser.
October 28, 2025
Vibration Engineering
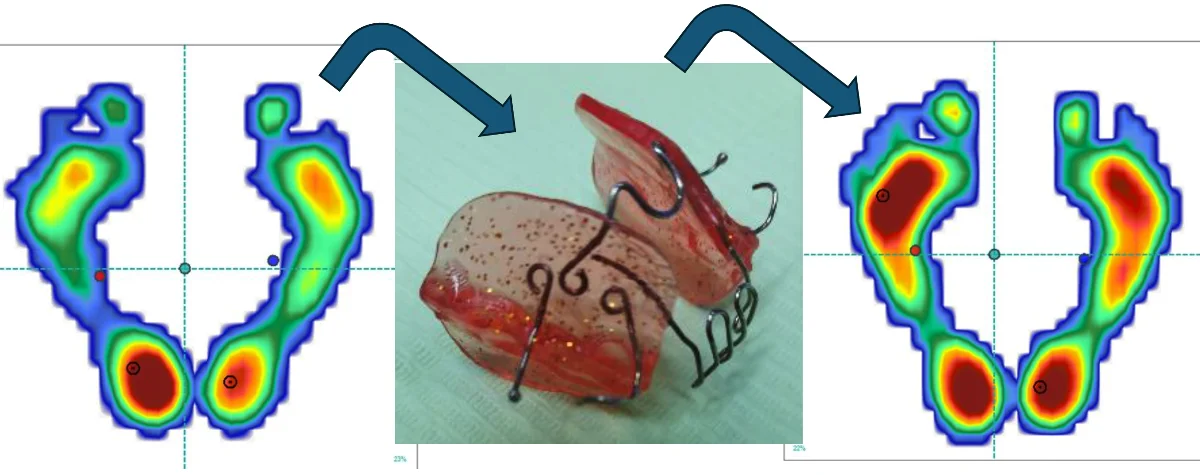
Research Article
The effect of Cranial Postural Balance (CPB) appliance on re-establishing mandible and body posture in an adult patient. Case report
This case report intends to present a functional appliance designed by the first author, that follow the principles expected for all functional appliances. It is not anchored on teeth. It does not produce mechanical forces and uses tongue and mandible posture change as natural forces. The appliance was used for 24 months, only to sleep. The patient came complaining discomfort with improper occlusion of the teeth and temporomandibular pain. Body balance was evaluated by DIERS and was also altered. It was possible to find out the presence of a unilateral crossbite and alteration on condyle position inside the cavity evaluated by CBCT. After the treatment with CPB (Cranial Posture Balance) appliance associated with osteopathic procedures, the occlusion and the temporomandibular complains were improved.
October 11, 2025
Orthopedics
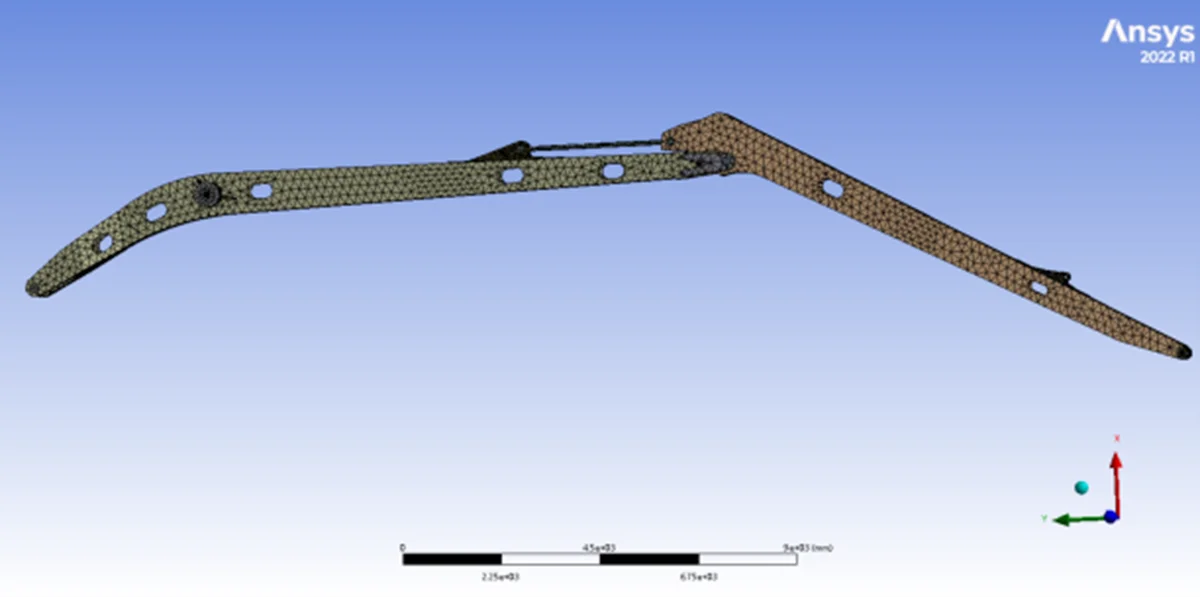
Research Article
EX1200 excavator structure simulation and analysis
This study investigates the structural optimization, lightweight design, and fatigue life influencing factors of the excavator working device through comprehensive static and dynamic finite element analysis (FEA). Modal analysis, spectral analysis, and vibration transfer path identification were conducted to assess the vibration response and fatigue failure risks at key joints such as the forearm pinholes. The inclusion of figures, such as vibration paths and stress distribution plots (see Figs. 3-8), supports the findings. The research provides a theoretical basis for assessing the structural reliability and fatigue life of long-arm excavators exceeding 25 meters.
September 30, 2025
Informatics
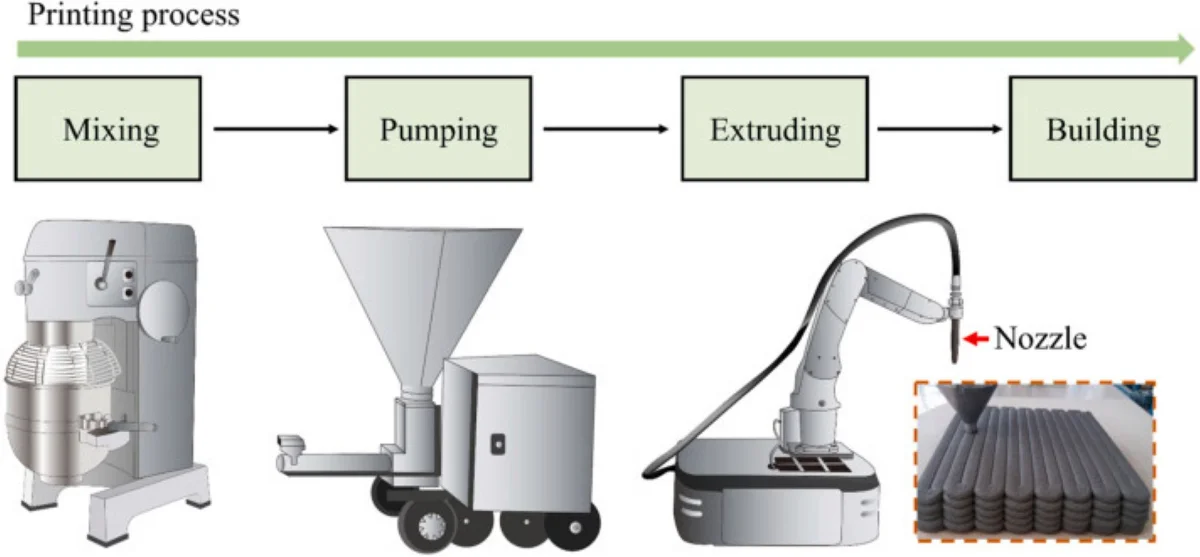
Research Article
Research progress on 3D printed geopolymer materials
The integration of 3D printing technology with geopolymer materials offers a sustainable alternative to conventional construction methods, significantly reducing CO2 emissions. However, challenges such as rapid setting, limited workability, and weak interlayer bonding limit their broader application. This review summarizes recent progress in 3D printed geopolymer composites, focusing on materials selection, rheological optimization, buildability, and mechanical performance enhancement. Strategies including the use of rheology modifiers, fiber reinforcements, nano-additives, and process optimization have shown promise in improving printability and structural performance. Remaining challenges, such as balancing setting time and printability and enhancing interlayer adhesion, are also discussed. Future research directions are proposed to further advance the development of high-performance, low-carbon geopolymer 3D printing materials for sustainable construction.
September 30, 2025
Applied Physics
Recently published
Research article
September 30, 2025
Traffic noise testing and collaborative control of elevated and ground-level composite roads
By Wen Zhang, Yuan Zheng, Chunzheng Liu, Ying Xu, Tang Tang
Recently published
Research article
September 24, 2025
Structural damage detection by progressive continuous wavelet transform and singular value decomposition of noisy mode shapes
By Shuigen Hu, Zhichun Ding, Shuping Liu, Qingyang Wei, Drahomír Novák, Maosen Cao
Best of engineering
Editor's pick
Research article
August 24, 2025
Bearing fault diagnosis based on multi-scale spectral images and convolutional neural network
By Tongchao Luo, Mingquan Qiu, Zhenyu Wu, Zebo Zhao, Dingyou Zhang
Editor's pick
Research article
July 18, 2025
Vibration and noise performance analysis and optimal design of V-rotor in permanent magnet synchronous motor: a new strategy for high efficiency and low noise
By Dawei Gu, Dashuai Shi, Zhengqing Liu, Zhuo Xu, Baisong Pan, Tie Geng, Bangchun Wen
Editor's pick
Research article
July 16, 2025
Small targets detection in low-resolution remote sensing images based on super-resolution joint optimization
By Bo Huang, Jian Lin, Enqi Huang, Liaoni Wu, Yiqing Cao
Editor's pick
Research article
June 4, 2025
Feedback torque control of an arm exoskeleton to assist user movement
By Thang Cao Nguyen, Ngoc Tuan Nguyen
You might also like
Most downloaded
Research Article
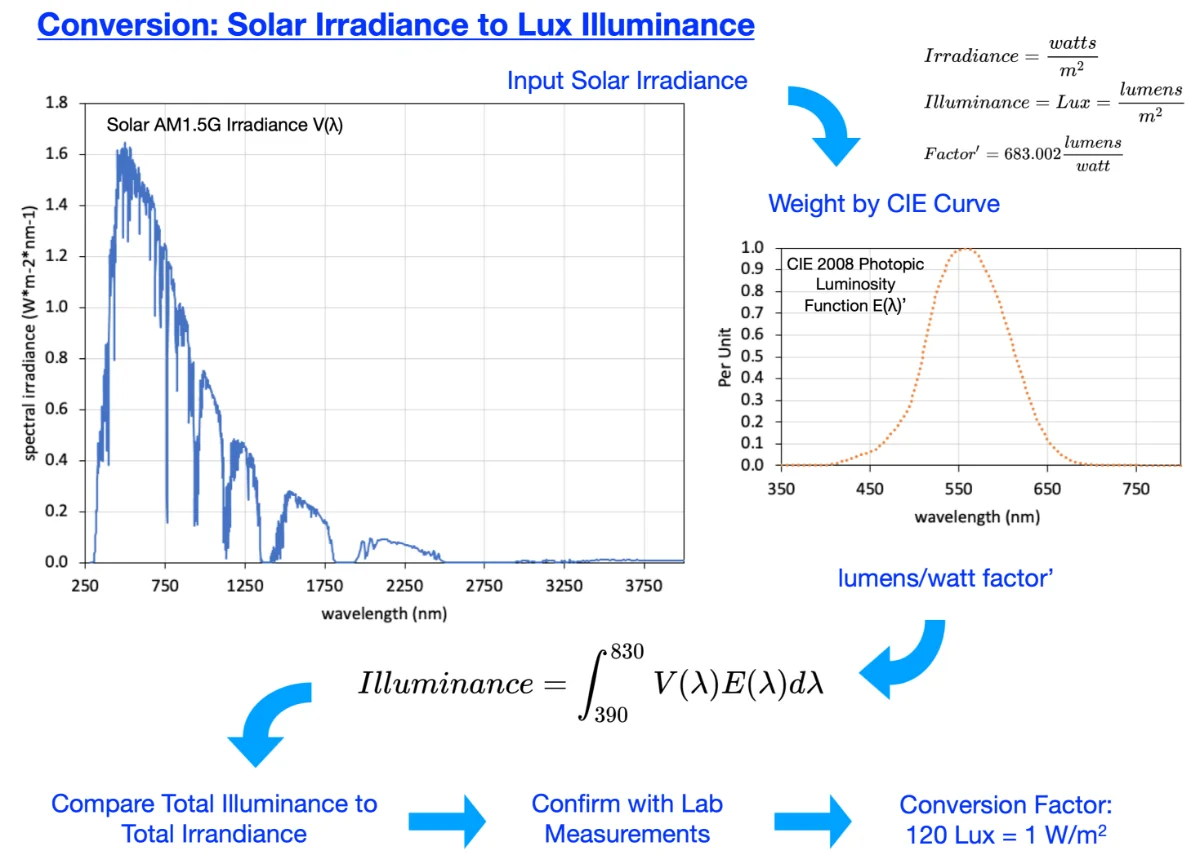
A conversion guide: solar irradiance and lux illuminance
By Peter R. Michael, Danvers E. Johnston, Wilfrido Moreno
The standard for measuring solar irradiance utilizes the units of watts per meter squared (W/m2). Irradiance meters are both costly and limited in the ability to measure low irradiance values. With a lower cost and higher sensitivity in low light conditions, light meters measure luminous flux per unit area (illuminance) utilizing the units of lumens per meter squared or lux (lx). An effective conversion factor between W/m2 and lx would enable the use of light meters to evaluate photovoltaic performance under low solar irradiance conditions. A survey of the literature found no definitive and readily available “rule of thumb” conversion standard between solar irradiance and illuminance. Easy-to-find Internet sources contain conflicting and widely varying values ranging from 688449 to 21000 lx for 1000 W/m2 (1 Sun) of solar irradiance. Peer-reviewed literature contains Luminous Efficacy equivalent values ranging from 21 to 131 lx per W/m2. This manuscript explores the relationship and establishes a theoretical and laboratory measurement guide for the conversion between solar irradiance and illuminance. The conversion factor includes standards data, equipment calibration accuracy, and uncertainty estimates. Solar Irradiance of 1 Sun (1000 W/m2) for an LED-based solar simulator is (116 ± 3) klx and (122 ± 1) klx for outdoor sunlight.
December 4, 2020
Applied Physics
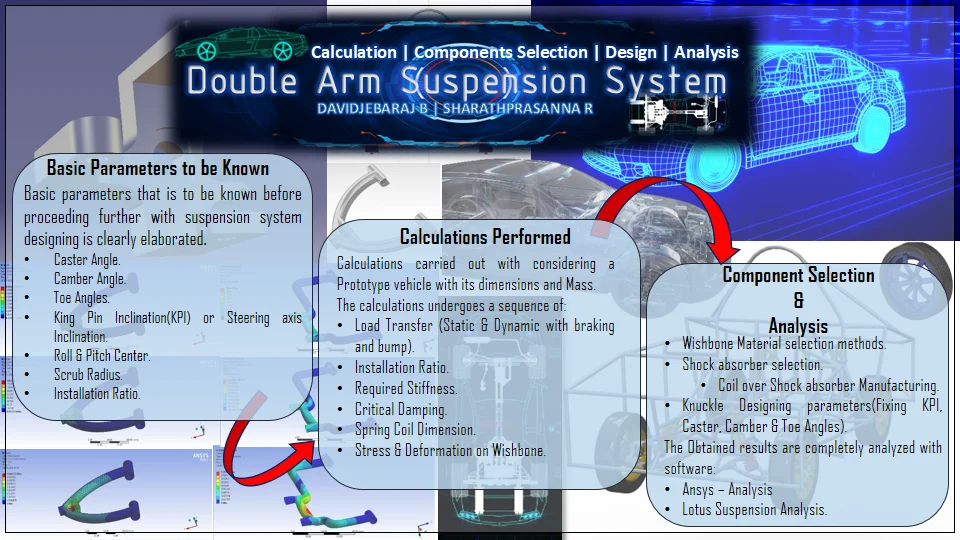
Most downloaded
Research Article
Design and calculation of double arm suspension of a car
By David Jebaraj B, Sharath Prasanna R
Suspension system is one of the challenging portions in designing a vehicle. The complete stability of the vehicle under dynamic conditions depends on the suspension system of the vehicle. Suspension system of a vehicle is interlinked with other systems such as steering, Wheels and Brakes. The main objective of this document is to provide complete guidance in designing and calculation of an independent suspension system with double control arms. The required parameters are calculated on considering a prototype vehicle with gross weight of 350 kg such as required stiffness of shock absorbers, Ride frequency, Motion ratio, Coefficient of damping etc. A CADD model was made with CATIA v5 r20 and SOLIDWORKS on the basis of calculations obtained and stress analysis was carried out for this model in various software such as Ansys. The complete assembled model was tested in LOTUS Shark and the result was obtained.
June 30, 2020
Industrial Engineering
Modal finite element analysis of PCBs and the role of material anisotropy
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are epoxy resin-impregnated and cured sheets of counter woven glass fabric (e.g. FR4) laminated between thin sheets of Copper. The nature of the PCB is inherently anisotropic and inhomogeneous but previous modal FEMs of PCBs have assumed isotropic, anisotropic (transversely isotropic and orthotropic) material properties and shown good correlation with test data for specific scenarios [1-3]. This paper details part of a research program aimed at gaining a better understanding of accurately modeling PCB’s dynamic behavior. New investigations into the impact of material anisotropy and, in particular, the effect of material orthogonal plane definition (Ex and Ey) on eigenfrequencies is analysed. A modal FEM of a JEDEC PCB is created, verified, and validated using well established theories by Steinberg and empirical data by others [4, 5]. The relative contributions of Ex, Ey and Ez on PCB eigenfrequencies is examined using a parametric modal FEM, analysing the role of material isotropy verses anisotropy. The impact of transversely isotropic material properties is also analysed for a typical JEDEC PCB. This analysis details the mesh density required for accurately modeling the PCB eigenfrequencies. The results show that a 100 % increase in Ez has only a 0.2 % difference in the eigenfrequency where as a 100 % increase in Ey has a 1.2 % difference in the eigenfrequency. The effect of orthotropic plane definition (alternating Ex with Ey) on the JEDEC PCB amount to a 7.95 % delta in eigenfrequency.
Coilgun design and evaluation without capacitor
Capacitors with high voltage and capacity values are used in most induction coilguns that are designed and constructed. The fact that capacitors are quite bulky and slow in energy transfer and how a coilgun can be made without using capacitors is the study subject of this article. Two and four coil gun samples were made to find the essential components of an electric gun, and the results are reported in this article. The accuracy of the results is also confirmed by FEMM analysis for these models. The harmony of experimental and theoretical results shows that smaller and low cost portable electrical weapons can be a powerful alternative to firearms in the future.