Basic Sciences

Journal of Measurements in Engineering
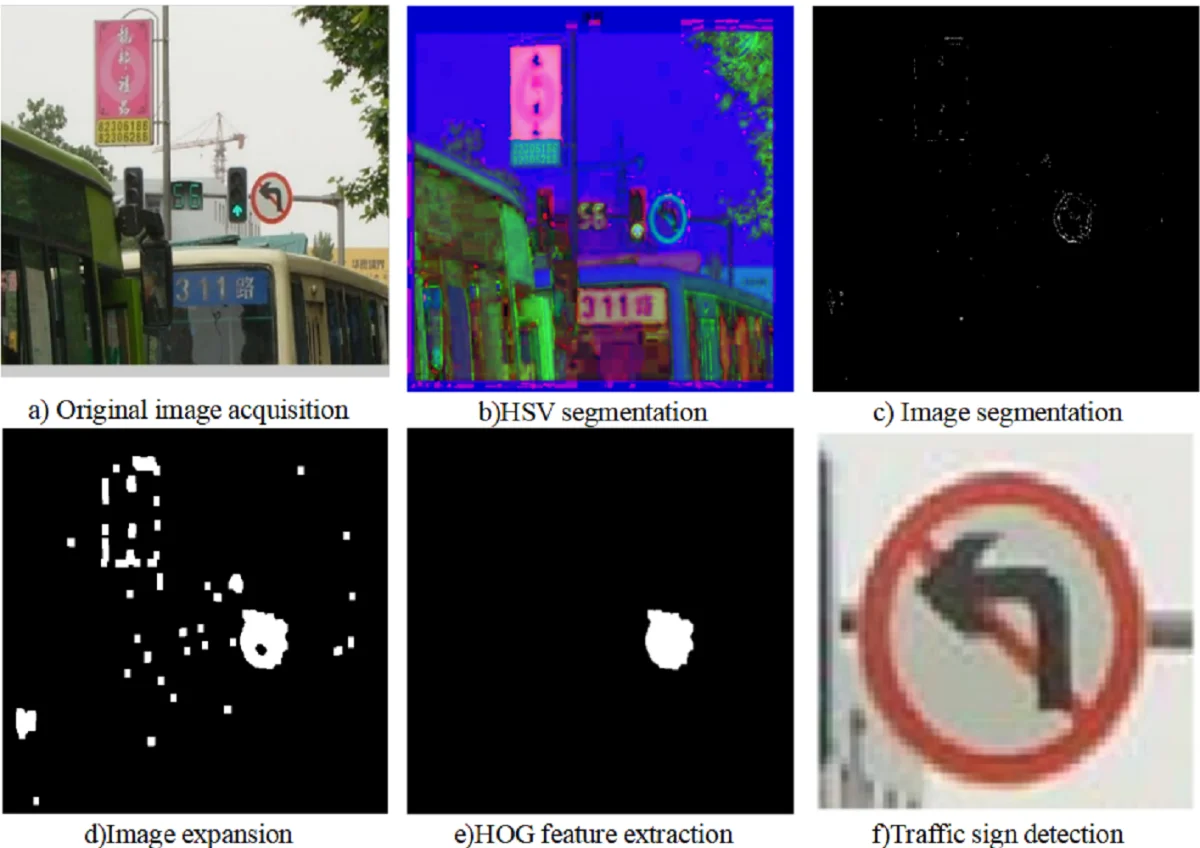

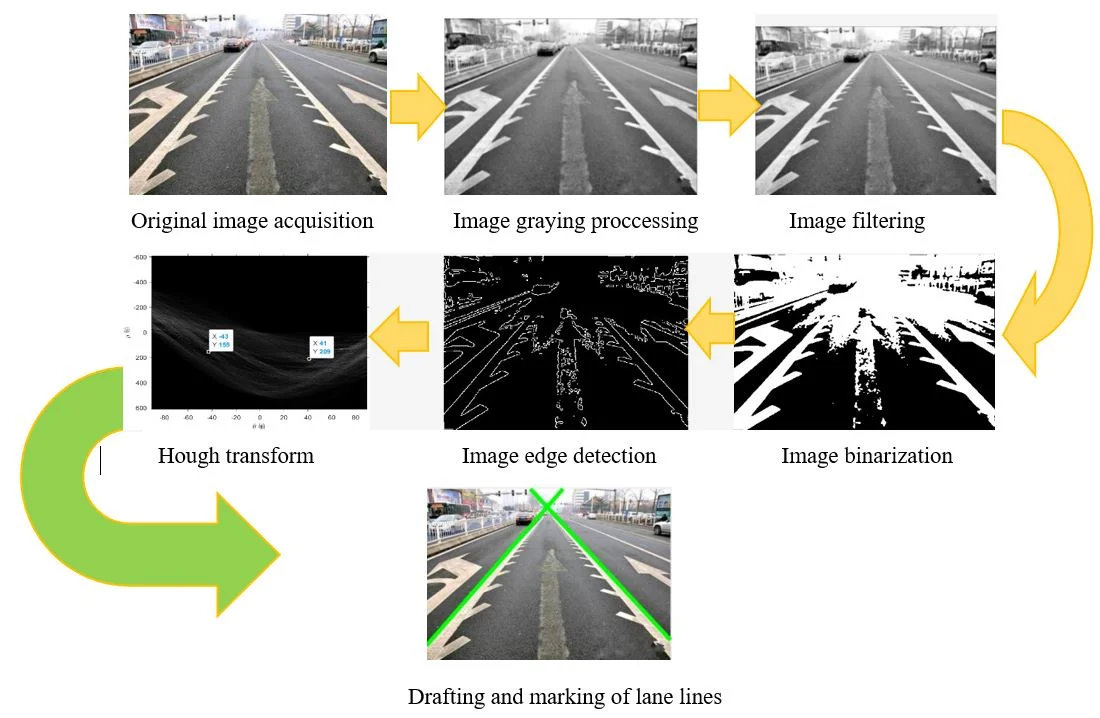
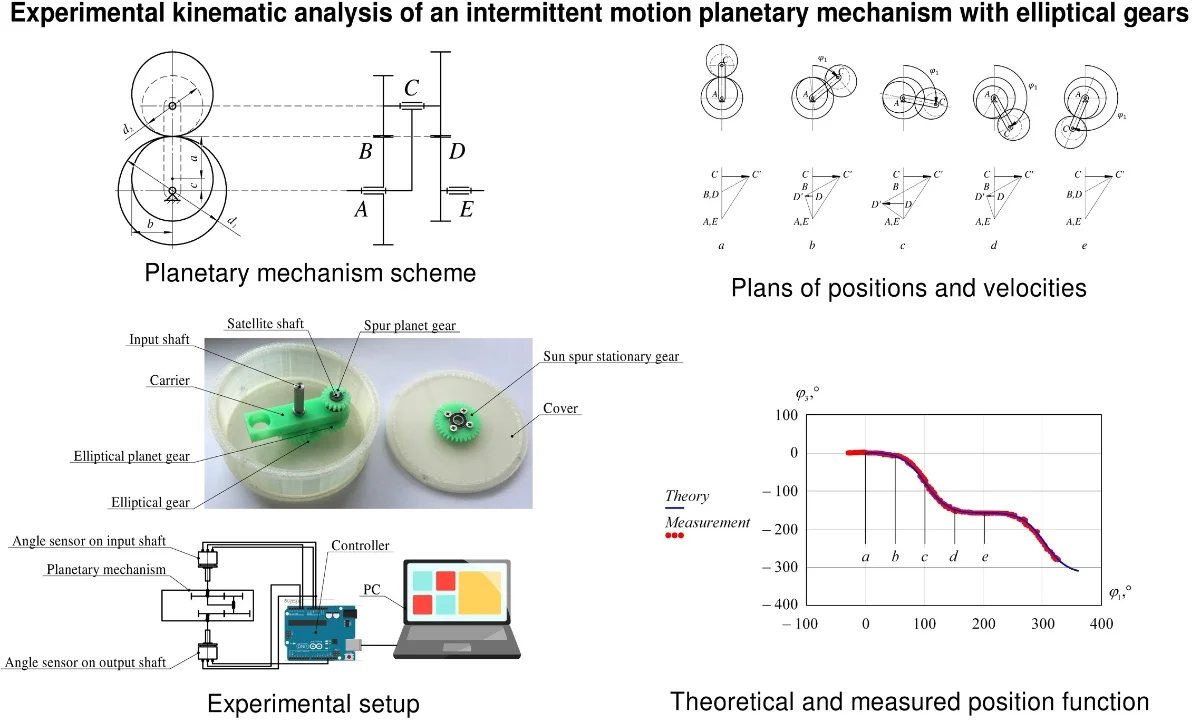
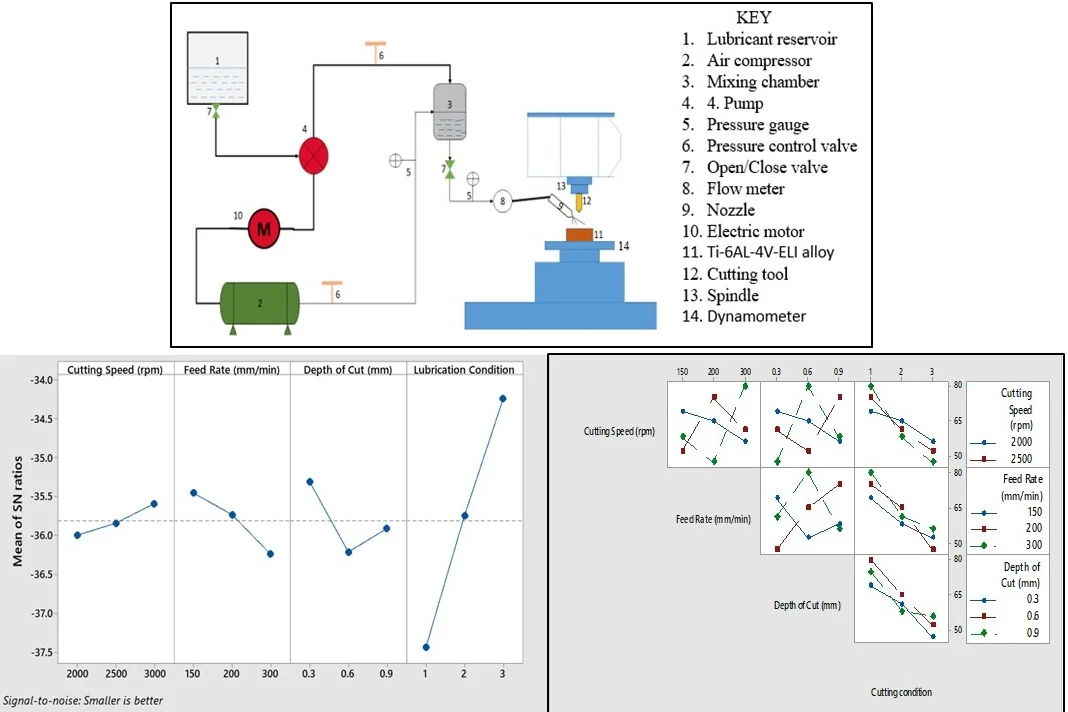
Best of Theme
You might also like
Understanding Basic Science
Welcome to Basic Science News on Extrica, a premier destination for those who yearn to understand the underpinnings of the scientific world. Basic science, the foundation upon which all complex scientific concepts are built, is an exploration into the fundamental principles that govern our universe. This section serves as a window into what basic science is: an exploration of core principles that form the bedrock of scientific knowledge.
How Basic Science Affects Everyday Life
Often, the significance of basic science in our daily lives goes unnoticed. Yet, its influence is all-encompassing, shaping everything from the technology we use to the medical treatments we receive. Basic science research acts as a catalyst for major advancements, laying the groundwork for applied science and subsequently, technological innovation. Understanding basic science facts is not just for academics but for anyone curious about the mechanics of their everyday world.
What to Expect in This Section
Our Basic Science News section provides a comprehensive collection of basic science articles, research findings, and journals of basic science. Expect to delve into a plethora of topics - from the basic science of public health to the foundational principles of psychology and medical education. This section is a treasure trove of basic science information, designed to enrich your basic science knowledge.
Leading Innovations in Basic Science
Staying abreast of the leading innovations in basic science is crucial for both academic and practical pursuits. This section highlights the groundbreaking basic science research that is pushing the boundaries of what we know. From new basic science theories to advancements in basic science topics, our coverage ensures that you are always informed about the cutting edge of basic science.
Contributing Experts in Basic Science
At Extrica, we pride ourselves on featuring content from a network of esteemed experts. Our contributing authors are not only scholars but also practitioners who bring a wealth of basic science knowledge and experience. Their insights bridge the gap between basic science and applied science, illuminating the real-world applications of these foundational principles.
Basic Science News on Extrica is more than just an open access journal; it's a dynamic platform where basic science principles come to life. Whether you are a student, educator, researcher, or simply a science enthusiast, this section is your gateway to understanding the basic science definition and its expansive scope. Join us in exploring the fascinating world of basic science on Extrica, where knowledge meets curiosity.