Abstract
The most important thing for condition based maintenance (CBM) is the maintenance decision-making, while the existing research mainly considers system maintenance decision-making from the economic point of view, but the actual situation is that the availability and safety of the system are more important in most cases. In this paper, the maintenance decision-making model of the system is established by giving priority to the availability and safety of the system, which is more in line with the engineering practice and lays a foundation for the application of condition based maintenance.
Highlights
- The availability model based on task for condition based maintenance is proposed
- The risk model based on safety for condition based maintenance is proposed
- The model is useful to improve the availability of maintenance decision
1. Introduction
Nowadays, condition based maintenance (CBM) of multi-component systems optimization is studied [1-4], and the relationship between the main popular maintenance modes is analyzed [5]. Many new methods are proposed, such as a new maintenance decision-making which is made by an artificial neural network, expert system and emulation technology is proposed to decrease the life cost [6]. The maintenance decision-making optimization is proposed considering the influence of human reliability to minimize the cost [7]. The discounted cost associated with a maintenance policy combining both condition-based and age-based criteria for preventive maintenance is proposed which provides a more realistic basis for optimizing the maintenance policies [8]. A cost-based selective maintenance decision-making method was presented considering the influence of machine failure intensity [1].
From the above description, we can know that the maintenance decision-making model is becoming more and more abounding and practical. However, the existing models are focusing on the cost, ignoring the availability model and risk model which are play a more important role in the maintenance decision-making. Therefore, we proposed the availability model based on task and risk model based on safety for condition based maintenance in this paper in order to obtain the maximum availability and expected risk for system.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. In Section 2 the availability model based on task and risk model based on safety for condition based maintenance is proposed. In Section 3, an experiment of gearbox is introduced. Then, the proposed method is applied to determine the gearbox optimal maintenance interval, which shows that different intervals will be obtained via the two models. Finally, the conclusions of the paper are drawn in Section 4.
2. Availability model and risk model
In actual engineering risk model based on safety is taken into account firstly to ensure the safety and the success of task. Secondly, availability model based on task is considered. In this paper, the components are assumed as well as new after maintenance. Moreover, maintenance decision-making model is proposed to determine the optimal maintenance interval.
2.1. Availability model based on task
In some cases, we can not only consider component economic efficiency, but also pay more attention to the task indicators. For example, we are more focused on availability and reliability of the aircraft, artillery and firearms in the battlefield, rather than how to reduce the cost. The economic factors will be considered only on the premise of ensuring availability. Then, the availability model based on task is needed to be established.
In an update cycle, the working time is consisted of as follows:
where Ti is optimal maintenance interval and ti is the ith monitoring time of system.
The time definition for a maintenance cycle is shown as follows:
where Tp is an average maintenance interval and Tf is average time for corrective maintenance.
The availability model is obtained as follows:
2.2. Risk model based on safety
In practice, the safety of the component is the most important. The purpose of maintenance decision-making is to realize accurate, timely and effective maintenance with decreasing maintenance costs at the same time. However, it does not mean that safety can be ignored. Once the safety problems occur, it may threaten the life safety of operating personnel or cause serious los. As a result, risk model based on safety need to be considered firstly.
The reliability or failure probability can be selected as the objective function in risk model based on safety. The optimal maintenance interval is determined through lower the fault probability of component to a pre-determined level. Assuming that component risk α, the failure rate cannot be higher than the risk α in every monitoring process. Therefore, the probability of component not failure is:
It can be described via the remaining useful life:
The maintenance interval of risk model based on safety can be obtained by Eq. (5) when the remaining useful life has been known.
The maintenance decision-making usually takes reliability or risk rate as the objective function under the security requirement. So, the failure probability reduced to an acceptable level is used to determine the optimal maintenance interval.
3. Application
3.1. The introduction of experiment
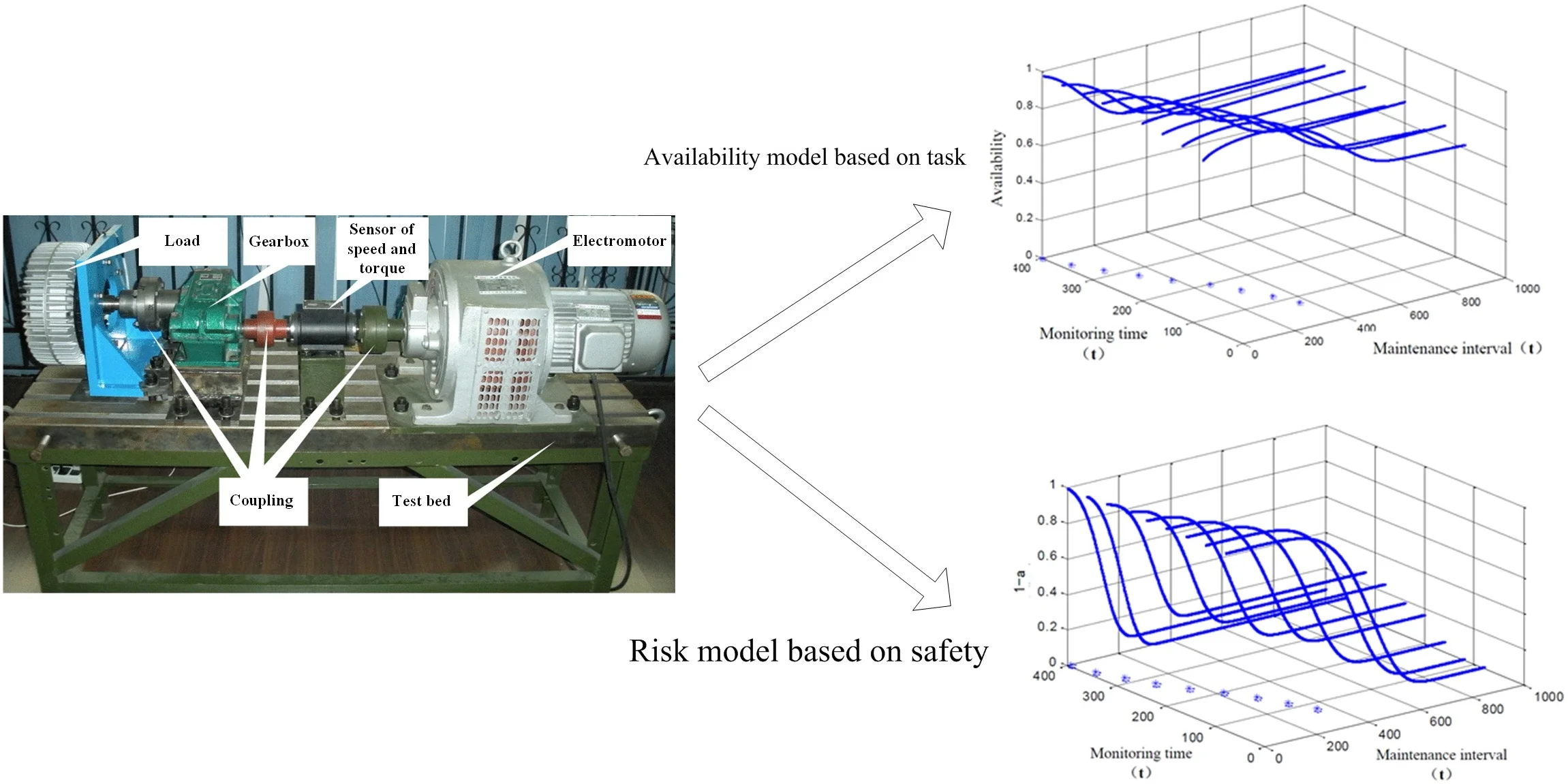
In the experiment, the gear box was driven by a electromotor, and a load was added to simulate the real working state of the gearbox. The gearbox is shown in Fig. 1, and test results are shown in Table 1.
Fig. 1The experiment of gearbox
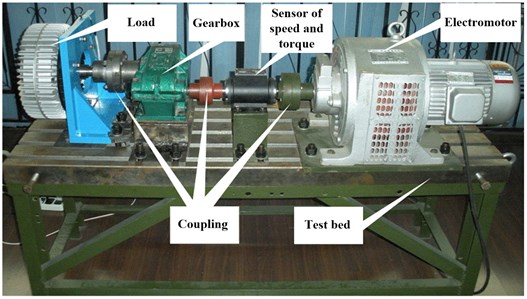
Table 1The test results
Monitoring time | 80 | 120 | 160 | 200 | 240 | 280 | 320 | 360 | 400 |
xi(h) | 361 | 321 | 281 | 241 | 201 | 161 | 121 | 81 | 41 |
Predicted RUL (h) | 434 | 382 | 305 | 268 | 210 | 182 | 144 | 127 | 60 |
3.2. The results analysis
In the experiment, we assume that Tp= 5 hours, Tf= 15 hours and the risk is α= 0.05. The results of availability model based on task is shown in Fig. 2.
Fig. 2The results of availability model based on task
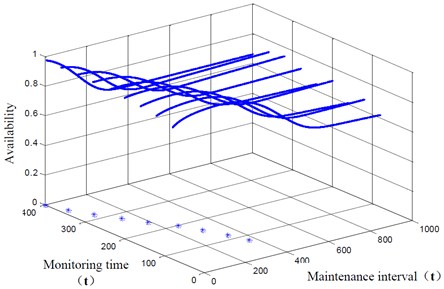
Table 2The results of availability model based on task
Monitoring point i | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
Ai | 0.9630 | 0.9634 | 0.9638 | 0.9647 | 0.9647 | 0.9665 | 0.9697 | 0.9730 | 0.9756 |
xi | 402 | 362 | 322 | 282 | 242 | 202 | 162 | 122 | 82 |
Ti | 370 | 343 | 298 | 256 | 189 | 140 | 82 | 34 | Repair immediately |
Prediction of RUL | 485 | 423 | 367 | 257 | 207 | 231 | 139 | 151 | 53 |
The results of availability model based on task is shown in Table 2, which we can determine the maintenance interval. When maintenance interval that determined by availability model is earlier than RUL, the decision for system is obtained via availability model. On the other hand, when maintenance interval that determined by availability model is later than RUL, maintenance decision-making is obtained based on RUL. As we can see from Table 2, maintenance interval is earlier than RUL at all time, so optimal maintenance interval for maintenance decision is all based on availability model.
In the risk model based on safety, we assume that risk α=0.05. Then, the result of maintenance decision-making based on risk model can be obtained which is shown in Fig. 3. As we can see from the figure, the safety index is higher with the decrease of the maintenance interval, which is consistent with our subjective experience. When 1-α> 0.95 is satisfied, we will get the most optimal maintenance interval.
Fig. 3The results of risk model based on safety
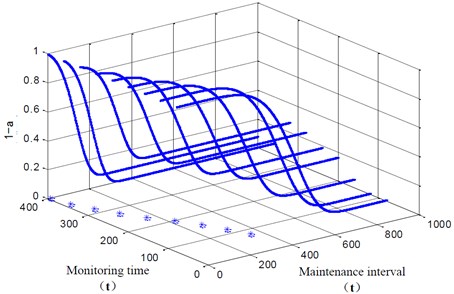
The results of risk model based on safety is shown in Table 3, which we can determine the maintenance interval. As we can see, the results based on risk model is earlier than the RUL of the gearbox, so it is necessary to propose maintenance decision based on risk model.
Table 3The results of risk model based on safety
Monitoring point i | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
xi | 402 | 362 | 322 | 282 | 242 | 202 | 162 | 122 | 82 |
Ti | 353 | 316 | 274 | 221 | 165 | 114 | 69 | 34 | 16 |
Prediction of RUL | 485 | 423 | 367 | 257 | 207 | 231 | 139 | 151 | 53 |
4. Conclusions
In actual engineering risk model based on safety is taken into account firstly to ensure the safety and the success of task. Secondly, availability model based on task is considered. In this paper, the availability model based on task and risk model based on safety for condition based maintenance is proposed, and the effectiveness of the method is verified by an experiment of gearbox. The availability model based on task and risk model based on safety is more in line with the actual situation of the project and can effectively improve the availability of maintenance decision.
References
-
Liu Fanmao, Zhu Haiping, Liu Boxing Maintenance decision-making method for manufacturing system based on cost and arithmetic reduction of intensity model, Journal of Central South University, Vol. 20, 2013, p. 1559-1571.
-
Jinmao Guo, Yaohui Zhang, Rui He, et al. The process of mission based maintenance decision-making for material. 3rd International Conference on Maintenance Engineering, Chengdu, China, 2012, p. 15-18.
-
Nipat Rasmekomen, Ajith Kumar Parlikad Condition-based maintenance of multi-component systems with degradation state-rate interactions. Reliability Engineering and System Safety, Vol. 148, 2016, p. 1-10.
-
Si Xiao Sheng, Wang Wenbin, Hu Chang Hua,et al. A Wiener-process-based degradation model with a recursive filter algorithm for remaining useful life estimation. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, Vol. 35, 2013, p. 219-237.
-
Zhou W., Nessim M. A. Optimal design of onshore natural gas pipelines. Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, Vol. 133, Issue 3, 2011, p. 031702.
-
Yang Mingzhong, Huang Jinguo, Zang Tiegang Research on an intelligent maintenance decision-making support system. International Journal of Plant Engineering and Management. Vol. 9, Issue 2, 2004, p. 85-90.
-
Asadzadeh S. M., Azadeh A. An integrated systemic model for optimization of condition-based maintenance with human error. Reliability Engineering and System Safety, Vol. 124, 2014, p. 117-131.
-
Vander Weide J. A. M., Pandey M. D., Van Noortwijk J. M. Discounted cost model for condition-based maintenance optimization. Reliability Engineering and System Safety, Vol. 95, 2010, p. 236-246.
About this article
The research is supported by National Engineering Laboratory for Mobile Source Emission Control Technology (No. NELMS2018C01), Science and Technology Directorate Project of Tianjin City (No. 18ZXSZSF00060) and the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei (No. E2019202198). The authors are grateful to all the reviewers and the editor for their valuable comments.

