Abstract
Graph theory, which has become a powerful area of mathematics, owns much advancement in the field of mathematical chemistry. Recently, chemical graph theory has turned into a very popular area among researchers because of its wide-ranging applications in the field of mathematical chemistry. The manipulation and inspection of chemical structural information is made feasible using molecular descriptors. The molecular topological descriptors are the numerical invariants of a molecular graph and are valuable for predicting their bioactivity. An abundant variety of such indices are taken into consideration and used in pharmaceutical researchers, in theoretical chemistry, in drugs and in several other fields. A topological index actually relates a chemical structure by means of a numeric number. In this recent research work, we have considered the chemical graph of magnesium iodide. We computed degree based topological indices. Mainly, we addressed atom-bond connectivity index (ABC), geometric arithmetic index (GA), fourth atom-bond connectivity index (ABC4), The fifth geometric-arithmetic index (GA5), general Randi index and First Zagreb index , Second Zagreb index for magnesium iodide, . Furthermore, the results are analysed and we have provided general formulas for all these above mentioned families of graphs that are in fact very helpful in studying the underlying topologies.
1. Introduction
The branch of chemistry which deals with the chemical structures with the help of mathematical tools is called the mathematical chemistry. Chemical graph is a branch of mathematical chemistry which applies graph theory to mathematical modeling of chemical phenomena. In chemical graph theory a molecular graph is a simple graph in which atoms and chemical bonds between them are represented by vertices and edges respectively.
Chemical reaction network theory is an area of applied mathematics that attempts to model the behavior of real world chemical system. Since its foundation in the 1960s, It has attracted a growing research community, mainly due to its applications in biochemistry and theoretical chemistry. It has also attracted interest from pure mathematicians due to the interesting problems that arise from the mathematical structures involved.
Graph theory has provided chemist with a variety of useful tools, such as topological indices [1]. Molecular and molecular compounds are often modeled by molecular graph [2]. A molecular graph is a representation of the structural formula of a chemical compound in terms of graph theory, whose vertices correspond to the atoms of the compound and edges corresponds to chemical bonds.
The concept of topological indices came from Harold Wiener while he was working on boiling point of paraffin, named this index as path number. Later on, the path number was renamed as Wiener index, defined as half of the sum of distances between all ordered pairs of vertices in a graph. That is the Wiener index of a connected graph is defined as [3]:
where is any ordered pair of vertices in and is the distance between the vertices and . The first degree-based topological index was put forward in 1975 by Millan Randic in his seminal paper “on characterization of molecular branching”, his index was defined as [4]:
with summation going over all pairs of adjacent vertices of the molecular graph , Randic himself named it “branching index”. Then Pal Erdos, one most famous mathematician, together with Bela Bolloba envisaged the beautiful but tough mathematics hidden in Randic index, Analyzing the structure-dependency of total -electron energy [5] an approximate formula was obtained in which terms of the form:
occurs, and among topological indices and named them “Zagreb group indices”.
Let be the edge of the molecular graph of , connecting the vertices u and v. Then the term in the definition of the Randic index, is the product of the degrees of the end-vertices of the edge e. The degree of this edge, i.e.., the number of edges adjacent to e is equal to . In order to take also this information into account, Ernesto Estrada conceived a new topological index, He named it “atom-bond connectivity index” which is conveniently abbreviated by ABC. it is defined as [6]:
From the success of ABC-index, Furtula et al, introduce its modified form, which is named as “augmented Zagreb index”. it is defined as [7]:
If we compared augmented Zagreb index formula with the ABC-index, instead of exponent 3, we set –0.5, then it became ordinary ABC index. another recently conceived vertex-degree-based topological index utilizes the difference between the geometric and arithmetic means, and is defined as [8]:
The index was invented byVukicevic and Furtula and was named “geometric-arithmetic index”. The so-called “sum-connectivity index” is a recent invention by [9]:
In the 1980s, Siemion Fajtlowics created a computer program for automatic generation of conjectures in graph theory. Then he examined the possible relations between countless graph invariants:
Then in [10] re-introduced this quantity, and called it “harmonic index”.
2. Methodology
Magnesium iodide is the name for the chemical compounds with the formulas and its variou hydrates , which is inorganic compound. These salts are typical ionic halides, being highly soluble in water.
Magnesium iodide has many commercial uses also, used to get different compounds for organic synthesis. Magnesium iodide is generally immediately available in most volumes, High purity, submicron and nanopowder forms may be considered. Iodide compounds are used in internal medicine. Treating an iodide with manganese dioxide and sulfuric acid sublimes the iodine. Magnesium iodide can be obtained from magnesium oxide, magnesium hydroxide, and magnesium carbonate by reaction with hydro-iodic acid:
The construction of is such that the every heptagone are connected to each other in column wise and rows the connection of heptagons is achieved by making three inside one haptagone. For our convenience, we take as the number of uper sides of in rows whereas n being the number of in lower side of heptagone.
Fig. 1Graph of magnesium iodide
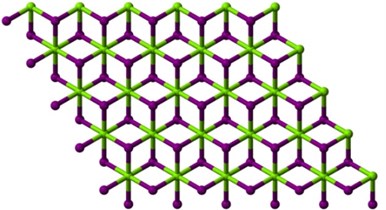
In the given graph, there are two variables and which are dependent on each other to maintain the structure of magnesium iodide. Magnesium having 2 electrons in its outermost shell, while iodide containing 7 electrons in its valence shell. To become stable and to react with other chemical element require some more electrons. Therefore, magnesium give its electron to iodide to become stable. To maintain the chemical structure of magnesium iodide, it depends on each other. Therefore, we sub-divided the graph between even and odd vertices respectively. The cardinality of vertices and edges in are and where respectively.
Fig. 2Molecular description of magnesium iodide
Table 1Edge subdivision of MgI2 based on degrees of end vertices of each edge for m=2n+1 where n≥1
Frequency | |
(3, 3) | 3 |
(3, 6) | 27 – 13 |
(2, 6) | 2 + 8 |
(3, 5) | 12 |
(2, 5) | 8 |
(3, 4) | 1 |
(1, 3) | 1 |
(1, 4) | 1 |
(1, 6) | + 5 |
(3, 2) | 2 |
(4, 2) | 2 |
Table 2Edge partition of MgI2 based on degrees of end vertices of each edge for m=2n+2 where n≥1
Frequency | |
(3, 3) | 3 + 1 |
(3, 6) | 27 + 7 |
(2, 6) | 2 + 8 |
(3, 5) | 2 |
(2, 5) | 2 |
(1, 3) | 1 |
(1, 5) | 1 |
(1, 6) | + 5 |
(3, 2) | 6 |
(2, 2) | 5 |
3. Results
In this section we have presented our main results, computed degree based topological indices for sum of end vertices on magnesium iodide.
Theorem 1. Let be the graph of magnesium iodide with where then its first Zagreb index is equal to .
Proof. First Zagreb index is given by:
Theorem 2. Let be the graph of magnesium iodide with where then its second Zagreb index is equal to .
Proof. Second Zagreb index is given by:
Theorem 3. Examine the graph with where 1 then its Randic index is equal to:
for
Proof. For , Randic index is given by:
Theorem 4. Examine the graph with where then its Randic index is equal to:
for .
Proof. For , Randic index is given by:
Theorem 5. Examine the graph with where then its Randic index is equal to for .
Proof. For , Randic index is given by:
Theorem 6. Examine the graph with where then its Randic index is equal to:
for .
Proof. For , Randic index is given by:
Theorem 7. Let be the graph of magnesium iodide with where 1 then its geometric arithmetic index is equal to:
Proof. Geometric arithmetic index is given by:
Theorem 8. Suppose the graph with where 1 then its atom-bond connectivity index is equal to:
Proof. Atom bond connectivity index is given by:
Theorem 9. Let be the graph of magnesium iodide with where 1 then its first Zagreb index is equal to
Proof. First Zagreb index is given by:
Theorem 10. Let be the graph of magnesium iodide with where then its second Zagreb index is equal to
Proof. Second Zagreb index is given by:
Theorem 11 Suppose the graph with where then its Randic index is equal to:
for
Proof. For , Randic index is given by:
Theorem 12. Suppose the graph with where then its Randic index is equal to:
for .
Proof. For , Randic index is given by:
Theorem 13. Suppose the graph with where then its Randic index is equal to for
Proof. For , Randic index is given by:
Theorem 14. Suppose the graph with where then its Randic index is equal to:
for .
Proof. For , Randic index is given by:
Theorem 15. Examine the graph with where then its atom-bond connectivity index is equal to:
Proof. Atom bond connectivity index is given by:
Theorem 16. Let be the graph of magnesium iodide with where then its geometric arithmetic index is equal to:
Proof. Geometric arithmetic is given by:
There are some of topological indices, such as fifth geometric arithmetic and fourth atom-bond connectivity .
Table 3Edge partition of MgI2 based on degrees of sum of end vertices of each edge for m=2n+1 where n≥ 1
Frequency | |
(12, 12) | 2 |
(14, 15) | 2 |
(12, 6) | 2 |
(18, 17) | 7 |
(16, 18) | 3 |
(10, 13) | 6 |
(16, 13) | 6 |
(18, 15) | 2–1 |
(18, 18) | 21 – 10 |
(13, 17) | 4 |
(12, 14) | 2+ 7 |
(12, 9) | 2 |
(12, 18) | 2 |
(9, 15) | n |
(6, 14) | 4 |
(18, 14) | 3 + 9 |
(13, 15) | 1 |
(15, 8) | 1 |
(14, 17) | 1 |
(14, 13) | 1 |
(13, 9) | 1 |
(8, 13) | 1 |
(10, 14) | 1 |
(10, 8) | 1 |
(6, 9) | 1 |
(8, 4) | 1 |
(9, 8) | 1 |
(3, 6) | 1 |
(8, 8) | 1 |
(8, 14) | 1 |
(9, 14) | 1 |
Table 4Edge sub-division of MgI2 based on degrees of sum of end vertices of each edge for m=2n+2 where n≥1
frequency | |
(5,8) | 4 |
(17,8) | 4 |
(17,18) | 10 |
(16,14) | 5 |
(12,14) | 8 |
(6,12) | 3 |
(12,18) | 3 |
(18,18) | 21 |
(9,15) | 1 |
(9,12) | 2 1 |
(17,14) | 7 |
(5,11) | 2 |
(11,17) | 2 |
(9,11) | 1 |
(11,14) | 1 |
(11,11) | 1 |
(12,12) | 1 |
(9,14) | 1 |
(6,9) | 1 |
(3,6) | 1 |
(17,17) | 1 |
(11,13) | 1 |
(11,7) | 1 |
(5,7) | 1 |
Theorem 17. Let be the graph of magnesium iodide with where then its index is equal to:
Proof. Atom bond connectivity index is given by:
Theorem 18. Suppose the graph with where then its index is equal to:
Proof. Geometric arithmetic index is given by:
Theorem 19. Suppose the graph with where 1 then its index is equal to:
Proof. Atom bond connectivity index is given by:
Theorem 20. Consider the graph with where then its index is equal to:
Proof. Geometric arithmetic index is given by:
4. Conclusions
We have studied the chemical graph of magnesium iodide and we subdivided the graph in even and odd vertices. Degree based topological indices for ABC, GA, ABC4, GA5, general Randic index and Zagreb index for magnesium iodide, has been computed in this research. Moreover, we have also given general formulas of these indices that can be very useful in studying the underlying topologies.
References
-
Gutman I. Degree-based topological indices. Croatica Chemica Acta, Vol. 86, 2013, p. 351-361.
-
Gutman I. Molecular graphs with minimal and maximal Randic indices. Croatica Chemica Acta, Vol. 75, 2002, p. 357-369.
-
Gao W., Shi Y. Wiener index of gear fan graph and gear wheel graph. Asian Journal of Chemistry, Vol. 26, Issue 11, 2014, p. 3397-3400.
-
Gutman I., Furtula B. Recent results in the theory of Randic index. University of Kragujevac, Kragujevac, Macedonia, 2008.
-
Gutman I., Trinajstic N. Graph theory and molecular orbitals. Total π-electron energy of alternant hydrocarbons. Chemical Physics Letters, Vol. 17, 1972, p. 535-538.
-
Estrada E., Torres L., Rodriguez L., Gutman I. An atom-bond connectivity index: modelling the enthalpy of formation of alkanes. Indian Journal of Chemistry, Vol. 37A, 1998, p. 849-855.
-
Furtula B., Graovac B., Vukicevic A., D. Augmented Zagreb index. Journal of Mathematical Chemistry, Vol. 48, 2010, p. 370-380.
-
Vukicevic C., Furtula B. Topological index based on the ratios of geometrical and arithmetical means of end-vertex degrees of edges. Journal of Mathematical Chemistry, Vol. 46, Issue 4, 2009, p. 1369-1376.
-
Lucic B., Nikolic S., Trinajstic, Zhou B., Ivanis Turk. S. Novel Molecular Structure Descriptors - Theory and Applications II. University, Faculty of Science, Kragujevac, 2010.
-
Wu R., Tang Z., Deng H. A lower bound for the harmonic index of a graph with minimum degree at least two. Filomat, Vol. 27, Issue 1, 2013, p. 51-55.
-
Dobrynin A., Entringer R., Gutman I. Wiener index of trees: theory and applications. Acta Applicandae Mathematica, Vol. 66, Issue 3, 2010, p. 211-249.
-
Randic M., Characterization of molecular branching. Journal of the American Chemical Society, Vol. 97, Issue 23, 1975, p. 6609-6615.
