Abstract
A complete comparison of seismic behavior of the application of Diagonal and Chevron Viscous Damper in steel structures is presented in this paper. OpenSees software is used for the numerical modeling of structures. Fifteen numbers of earthquake records are applied to the structures and full nonlinear time history analysis is done. Force-displacement of chevron braces with and without a damper are compared and the results of IDA curves are also presented for different percentiles.
1. Introduction
There are two common types of steel chevron and diagonal bracing frames, equipped with viscose fluid damper are studied in this paper. All dimensional specifications, as well as the specifications of the cross-sections and materials used for the beams, columns, and braces of the frame models, are considered as similar. OpenSees software is used to model the structures and a suit of fifteen earthquake records are used for nonlinear time history analysis. Viscous dampers have a great displacement under strong ground motions and absorb earthquake energy and less damage will occur in structural components. It has been established that the base shear and displacements are decreased by using viscous dampers in steel structures. The main advantages of viscous dampers are on the hysteretic behavior in the main structural members. One of the most practical and effective methods for controlling the behavior of the structures is using viscous dampers. The designed procedures of dampers are based on the structural period, soil type and structural components. [1].
2. Structural modeling
In this research, there are four story steel frame structures with chevron and diagonal braces are studied and designed in ETABS software [1]. The height of each floor is 3 meters and the length of each bay is 5 meters. Viscous dampers in the OpenSees software have been placed at the junction of the beam and the column [2-5]. In Table 2, the details information of earthquake records is presented in Table 2. The record selection has been done from FEMA-P695. Incremental dynamic analysis (IDA) is used in this study to obtain the nonlinear behaviour of structures.
Table 1Sections assigned in each of steel frames
4-story structure with diagonal and chevron braces | ||
Column sections | Beam sections | Brace sections |
IPB 180 | IPE270 | TUBO 80*80*8 |
Table 2Specifications of far field and near field accelerograms [2]
Specifications of the Selected Records | |||||||
Record No. | Earthquake name | Station name | Year | Magnitude | Soil type | Fault type | PGA |
1 | Northridge | Beverly Hills-Mulhol-USC | 1994 | 6.7 | D | Thrust | 0.52 |
2 | Northridge | Canyon Country-WLC-USC | 1994 | 6.7 | D | Thrust | 0.48 |
3 | Duzce, Turkey | Bolu-ERD | 1999 | 7.1 | D | Strike-slip | 0.82 |
4 | Hector Mine | Hector-SCSN | 1999 | 7.1 | C | Strike-slip | 0.34 |
5 | Imperial Valley | Delta-ENAMUCSD | 1979 | 6.5 | D | Strike-slip | 0.35 |
6 | Imperial Valley | El Centro Array #11-USGS | 1979 | 6.5 | D | Strike-slip | 0.38 |
7 | Kobe, Japan | Nishi-Akashi-CUE | 1995 | 6.9 | C | Strike-slip | 0.51 |
8 | Kobe, Japan | Shin-Osaka-CUE | 1995 | 6.9 | D | Strike-slip | 0.24 |
9 | Kocaeli, Turkey | Duzce-ERD | 1999 | 7.5 | D | Strike-slip | 0.36 |
10 | Kocaeli, Turkey | Arcelik-KOERI | 1999 | 7.5 | C | Strike-slip | 0.22 |
11 | Landers | Yermo Fire Station-CDMG | 1992 | 7.3 | D | Strike-slip | 0.24 |
12 | Landers | Coolwater-SCE | 1992 | 7.3 | D | Strike-slip | 0.42 |
13 | Loma Prieta | Capitola-CDMG | 1989 | 6.9 | D | Strike-slip | 0.53 |
14 | Loma Prieta | Gilroy Array #3-CDMG | 1989 | 6.9 | D | Strike-slip | 0.56 |
15 | Manjil, Iran | Abbar-BHRC | 1990 | 7.4 | C | Strike-slip | 0.51 |
3. Incremental Dynamic Analysis (IDA)
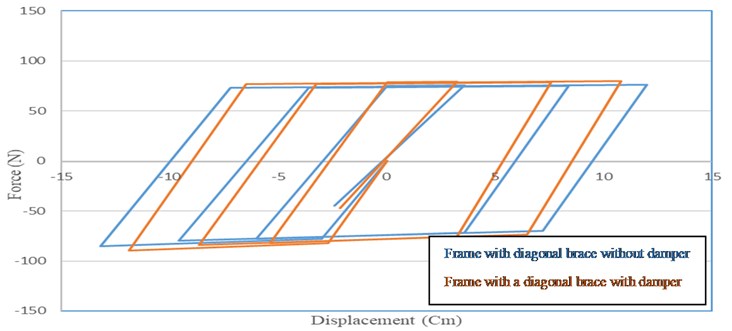
A full nonlinear time history analysis has been done based on the IDA procedure. The results of nonlinear time history have been shown in Figures 1 and 2. These figures shows the behavior of structures from linear to nonlinear levels. Maximum inter story drift is considered as an Engineering Demand Parameter (EDP) in diagonal and chevron bracing with a viscous damper and Sa (T1, 5%) as an Intensity Measures (IM). The results are for the frame with chevron bracing with a viscous damper and with diagonal bracing with a viscous damper. To better understanding of the performance of the structures, the nonlinear behavior of structural components is studied. Figures 3 is shown the hysteretic behavior of chevron braces with and without viscous dampers. Figure 4 is shown the hysteretic behavior of diagonal braces with and without viscous damper. The tight loops are the better performance of viscous structures.
Fig. 1Summary of IDA curves obtained for a 4-story structural frame with chevron bracing with a viscous damper
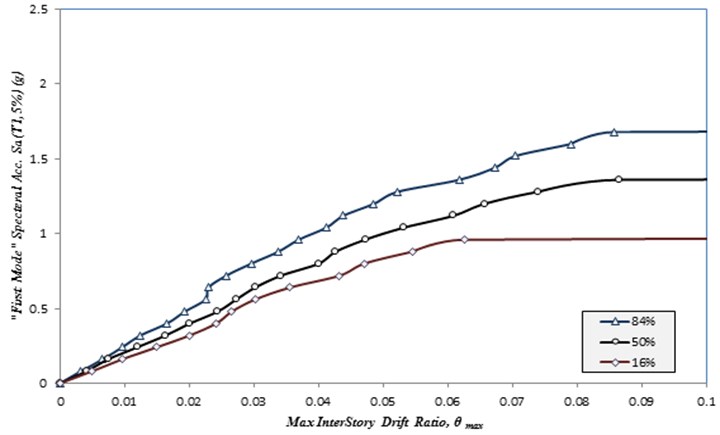
Fig. 2Summary of IDA curves obtained for a 4-story structural frame with diagonal bracing with a viscous damper
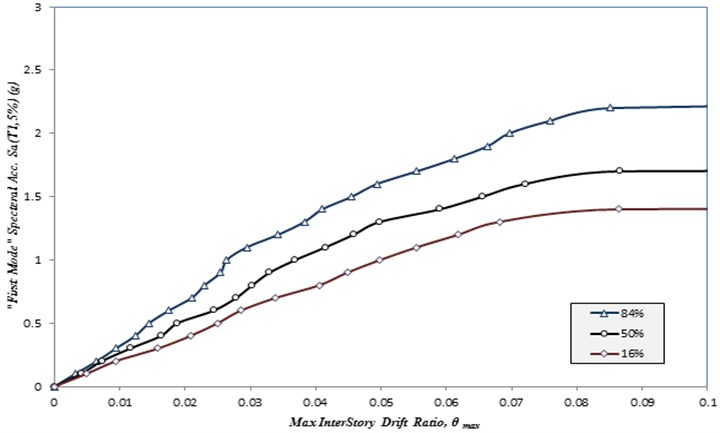
Fig. 3Comparison of the curves of the frame with chevron braces with and without damper
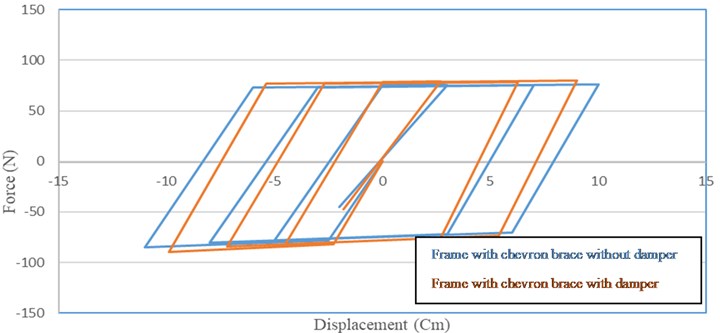
Fig. 4Comparison of the curves of the frame with diagonal braces with and without damper
4. Conclusions
In this paper, nonlinear behavior of steel frames with chevron and diagonal braces were considered. The effects of viscous dampers were considered in steel frames. The results show that the viscous dampers have a great effects on the hysteretic behavior of the steel frames and has less displacements. Chevron braces has better performance compared to the diagonal braces. The results indicate that the viscous dampers are improved the seismic performance of the structures.
References
-
ATC-58, Guidelines for Seismic Performance Assessment of Buildings. Applied Technology Council. Washington, D.C., 2011.
-
Quantification of Building Seismic Performance Factor. Report No. FEMA-P695. Federal Emergency Management Agency, Washington, D.C., 2009.
-
Baker J. W. Efficient Analytical Fragility Function Fitting Using Dynamic Structural Analysis. Stanford University, 2014.
-
Fanaien, Ezzatshoar S. Studying the seismic behavior of gate braced frames by incremental dynamic analysis (IDA). Journal of Constructional Steel Research, Vol. 99, 2014, p. 111-120, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2014.04.08
-
Soltangharaei V., Razi M., Gerami M. Comparative evaluation of behavior factor of SMRF structures for near and far fault ground motions. Periodica Polytechnica Civil Engineering, Vol. 60, Issue 1, 2016, p. 75-82, https://doi.org/10.3311/PPci.7625

